The 23rd Singapore International Bunkering Conference (SIBCON), organised by the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA), was opened today by Dr Amy Khor, Senior Minister of State for the Ministry of Sustainability and the Environment and the Ministry of Transport. Themed “Accelerating the Maritime Fuel Transition”, the biennial event, held from 8 to 10 October 2024, is expected to be attended by more than 2000 maritime professionals from 38 countries.
Digital Bunkering - The New Normal in the Port of Singapore from 1 April 2025
Speaking at the opening address, Dr Amy Khor announced that from 1 April 2025, all bunker suppliers will be required to provide digital bunkering services and issue electronic bunker delivery notes (e-BDNs) as a default. This announcement follows successful pilots conducted since 1 November 2023 with bunker suppliers, including the top 10 bunker players, in Singapore.
The digital bunkering process allows for efficient data sharing between bunker buyers and suppliers, which will help expedite administrative processes, improve accountability, ensure compliance with regulations, reduce the potential for errors, and support early detection of fraudulent activities. It also promotes a more streamlined, secured, and environmentally friendly bunkering process, which is expected to help industry save close to 40,000 man-days annually.
This represents a key milestone to further strengthen the competitiveness and efficiency of bunkering in Singapore since the Port of Singapore became the first port globally to adopt mass flow metering for custody transfers from 1 Jan 2017. Singapore will be the first port globally to implement digital bunkering at scale for all bunkering operations, and will continue to exchange our experiences with like-minded ports. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) accepted e-BDN as an equivalent format from July 2023.
To further enhance transparency and transaction integrity in bunkering operations, MPA will also introduce a centralised e-BDN record verification facility. This enables key stakeholders to verify the e-BDN received against the information transmitted to MPA. In addition, Enterprise Singapore (EnterpriseSG), through the Singapore Standards Council (SSC), will launch a new Singapore Standard (SS) 709 Specification for Digital Bunkering Supply Chain Documentation, to ensure data consistency and interoperability between digital systems and facilitate smoother transactions through trusted and verifiable digital bunkering documents. EnterpriseSG has also launched the revised Singapore Standard (SS) 648 Code of Practice for Bunker Mass Flow Metering to include data integrity and transmission requirements in line with this new digital standard.
Reducing Business Costs and Rules Review
MPA has been working with industry and our unions to review rules and reduce business costs. In a related effort and after careful study, MPA will reduce the frequency for the verification of mass flow meters (MFM) from twice to once a year from 1 April 2025 in line with the updated SS648:2024 standards. This is expected to save the industry approximately $300,000 a year. Risk-based audits will continue as the bunker industry undertakes this transition.
This follows cost reduction efforts earlier in the year to waive the security deposits and banker’s guarantees for companies of low credit risk, and initiatives such as night-tows for container barges to reduce the turnaround time for barges from regional ports.
Adoption of Maritime Artificial Intelligence Products in the Port of Singapore
MPA has been co-developing maritime artificial intelligence products with industry and cloud providers. Maritime Singapore will benefit from two new MPA-developed AI-driven applications, DocuMind and DocuMatch, designed to significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of renewals of Singapore-registered ship certificates. DocuMind uses multi-modal Large Language Models to read information from various document formats. DocuMatch verifies the relevant data against internal databases and recommends application approvals. To be launched on 1 January 2025, these innovations are expected to enhance service levels to industry by accelerating certificate processing time from up to three days to within a few minutes for most transactions. MPA plans to apply the use of such AI-driven tools to more industry use-cases next year to bring about greater efficiency for all port users.
Facilitating a Multi-Fuel Bunkering Future
In the first eight months of 2024, Singapore saw strong growth of approximately 7% in total bunker sales over the same period last year, reaching over 36 million tonnes. Biofuels and liquefied natural gas bunker sales surpassed 700,00 metric tonnes. The Port of Singapore also conducted successful ship-to-containership and simultaneous container operations and bunkering operations for methanol, and terminal-to-ship bunkering of ammonia. MPA will continue to work closely with industry, unions, and research institutes to enhance training of maritime workers.
In July 2024, MPA and the Energy Market Authority (EMA) shortlisted two consortia, Sembcorp-SLNG and Keppel’s Infrastructure Division, in a restricted Request for Proposal (RFP), to advance to the next round of evaluations to provide a low- or zero-carbon ammonia solution on Jurong Island for power generation and bunkering.
Since then, the consortia have proposed two additional ammonia bunkering proposals from Mitsui & Co., Ltd and Fortescue-Equatorial Marine Fuels, which have been evaluated and selected. The two proposals, added to the existing three under the two shortlisted consortia, will be considered in the next round of the RFP process.
The development of multi-fuel bunkering capability in Singapore will help create new job opportunities in related fields, including trading, green technology, sales, legal, and finance.
To support the operationalisation of a higher mix of low-carbon alternative fuels, both EnterpriseSG and MPA are developing the Singapore standards for methanol bunkering and ammonia bunkering by 2024 and 2025 respectively. The standards will cover custody transfer requirements, safety procedures and crew competencies, to ensure safe bunkering operations and handling of these fuels.
Refreshed Maritime Singapore Green Initiative to Encourage Early Adoption of Green Fuels and Technologies
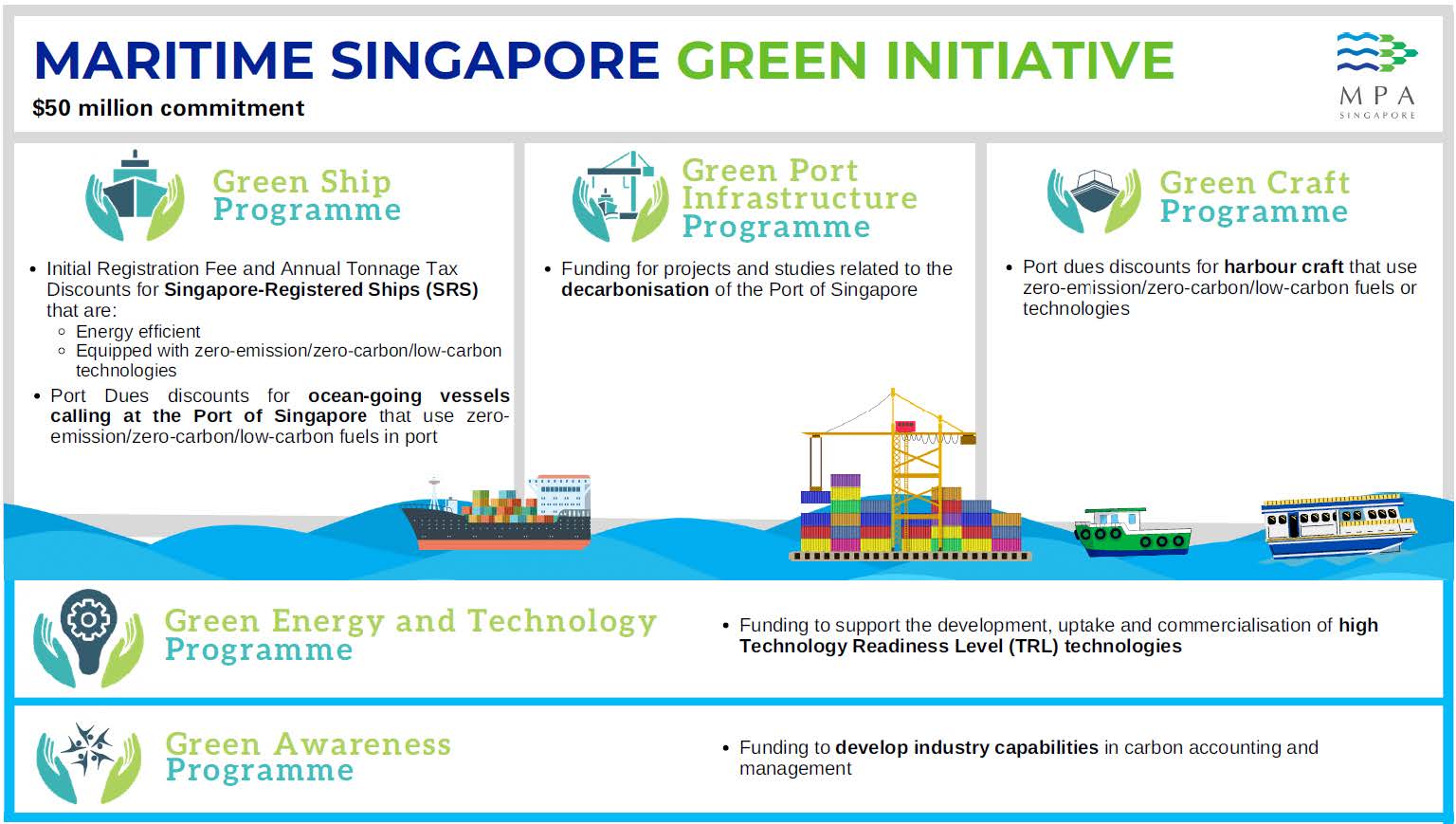
In line with the strengthened global commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from ships, MPA will continue to facilitate global negotiations currently underway at the IMO. MPA has updated various green initiatives and incentives under the Maritime Singapore Green Initiative (MSGI) to encourage early adoption of zero and near-zero emission technologies and fuels. MPA will commit $50 million to support the implementation of the refreshed MSGI. Please refer to Annex A for details.
Maritime Energy Training Facility Attracts New Partners
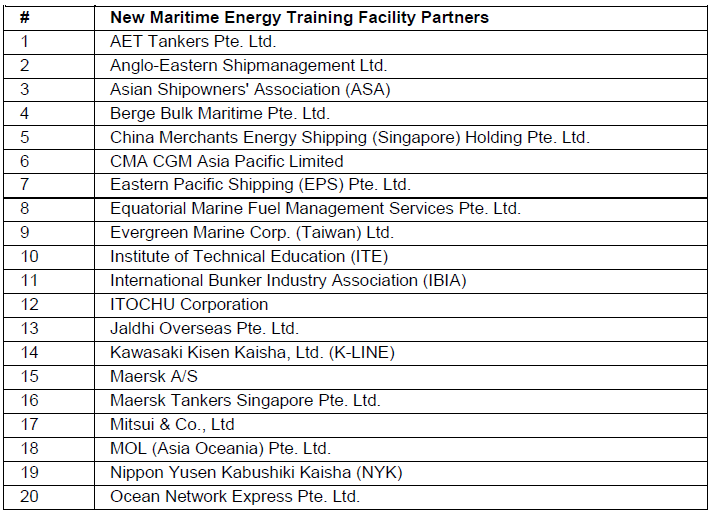
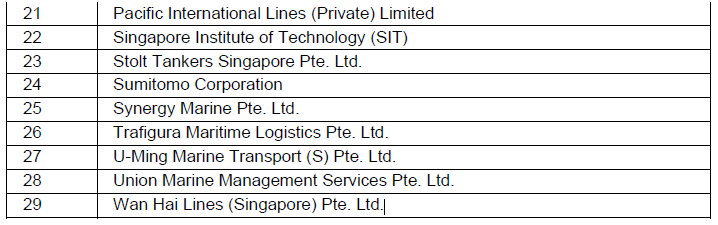
Dr Amy Khor also announced the onboarding of 29 new Maritime Energy Training Facility (METF) partners from various shipping companies, ship management companies, trading companies, maritime associations and institutes of higher learning. Please refer to Annex B for details. They add to the existing 22 partners. The new partners will collaborate with MPA to validate and shape METF’s training courses, including the training curriculum and curriculum delivery of courses on future fuels and technologies supporting maritime decarbonisation.
The industry’s growing support for METF reflects the strong interest and urgent need for new and enhanced training courses in the maritime sector to address the skills and competency gaps in operating vessels powered by zero or near-zero emissions fuels, such as methanol and ammonia.
Green and Digital Shipping Corridor (GDSC) Collaborations to Accelerate Decarbonisation and Digitalisation of International Shipping
Singapore-Shandong GDSC
Singapore and Shandong province of the People’s Republic of China have signed the Singapore-Shandong GDSC at the 25th Singapore-Shandong Business Council meeting co-chaired by Minister for Transport and Second Minister for Finance, Chee Hong Tat, and Governor of Shandong Provincial Government, Zhou Naixiang. Shandong is China’s second most populous province after Guangdong, with approximately 101 million people, and the third largest provincial economy in China after Guangdong and Jiangsu with a GDP of 9.2 trillion RMB (approximately 1.7 trillion SGD) and GDP growth of 6% in 2023. Together with the Singapore-Tianjin GDSC, these GDSCs support closer digital and green fuel collaboration between Singapore and the Bohai and Yellow Sea Region.
Singapore - Port of Los Angeles (LA)- Port of Long Beach (LB) GDSC
Three major shipping lines — Hafnia, K-Line, and MOL — are in early discussions to join the LA-LB-Singapore GDSC initiative. Each partner would be expected to spearhead a project to advance the corridor’s decarbonisation and digitalisation goals, such as the adoption of net-zero fuels, Just-in-Time route optimisation, and energy efficiency technologies such as wind-assisted ship propulsion. The addition of the new partners will significantly strengthen the GDSC’s capacity to drive innovation in sustainable shipping practices and accelerate the adoption of zero/near-zero emission fuels and green technologies along the corridor.
Singapore-Port of Rotterdam GDSC
The potential demand for zero or low-emission fuels from all shipping lines within the Singapore-Port of Rotterdam Authority (PoR) GDSC corridor was discussed at the GDSC stakeholder workshop conducted by MPA and the PoR in Rotterdam in September 2024. Based on current order books, there is a potential demand by 2028 for up to five million tonnes per year for greener variants of methane and methanol for more than 200 vessels along the corridor. The ports have also welcomed two new members – GATE Terminal and Singapore LNG Terminal – to the GDSC, to support efforts to develop a pilot trial and regulatory sandbox for bio-methane.
Singapore has entered into GDSC arrangements with Australia, China, Japan, Netherlands, and the United States of America, reflecting the multilateral approach and support for sustainable shipping.
ANNEX A
ANNEX B
source: MPA
Speaking at the opening address, Dr Amy Khor announced that from 1 April 2025, all bunker suppliers will be required to provide digital bunkering services and issue electronic bunker delivery notes (e-BDNs) as a default. This announcement follows successful pilots conducted since 1 November 2023 with bunker suppliers, including the top 10 bunker players, in Singapore.
The digital bunkering process allows for efficient data sharing between bunker buyers and suppliers, which will help expedite administrative processes, improve accountability, ensure compliance with regulations, reduce the potential for errors, and support early detection of fraudulent activities. It also promotes a more streamlined, secured, and environmentally friendly bunkering process, which is expected to help industry save close to 40,000 man-days annually.
This represents a key milestone to further strengthen the competitiveness and efficiency of bunkering in Singapore since the Port of Singapore became the first port globally to adopt mass flow metering for custody transfers from 1 Jan 2017. Singapore will be the first port globally to implement digital bunkering at scale for all bunkering operations, and will continue to exchange our experiences with like-minded ports. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) accepted e-BDN as an equivalent format from July 2023.
To further enhance transparency and transaction integrity in bunkering operations, MPA will also introduce a centralised e-BDN record verification facility. This enables key stakeholders to verify the e-BDN received against the information transmitted to MPA. In addition, Enterprise Singapore (EnterpriseSG), through the Singapore Standards Council (SSC), will launch a new Singapore Standard (SS) 709 Specification for Digital Bunkering Supply Chain Documentation, to ensure data consistency and interoperability between digital systems and facilitate smoother transactions through trusted and verifiable digital bunkering documents. EnterpriseSG has also launched the revised Singapore Standard (SS) 648 Code of Practice for Bunker Mass Flow Metering to include data integrity and transmission requirements in line with this new digital standard.
Reducing Business Costs and Rules Review
MPA has been working with industry and our unions to review rules and reduce business costs. In a related effort and after careful study, MPA will reduce the frequency for the verification of mass flow meters (MFM) from twice to once a year from 1 April 2025 in line with the updated SS648:2024 standards. This is expected to save the industry approximately $300,000 a year. Risk-based audits will continue as the bunker industry undertakes this transition.
This follows cost reduction efforts earlier in the year to waive the security deposits and banker’s guarantees for companies of low credit risk, and initiatives such as night-tows for container barges to reduce the turnaround time for barges from regional ports.
Adoption of Maritime Artificial Intelligence Products in the Port of Singapore
MPA has been co-developing maritime artificial intelligence products with industry and cloud providers. Maritime Singapore will benefit from two new MPA-developed AI-driven applications, DocuMind and DocuMatch, designed to significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of renewals of Singapore-registered ship certificates. DocuMind uses multi-modal Large Language Models to read information from various document formats. DocuMatch verifies the relevant data against internal databases and recommends application approvals. To be launched on 1 January 2025, these innovations are expected to enhance service levels to industry by accelerating certificate processing time from up to three days to within a few minutes for most transactions. MPA plans to apply the use of such AI-driven tools to more industry use-cases next year to bring about greater efficiency for all port users.
Facilitating a Multi-Fuel Bunkering Future
In the first eight months of 2024, Singapore saw strong growth of approximately 7% in total bunker sales over the same period last year, reaching over 36 million tonnes. Biofuels and liquefied natural gas bunker sales surpassed 700,00 metric tonnes. The Port of Singapore also conducted successful ship-to-containership and simultaneous container operations and bunkering operations for methanol, and terminal-to-ship bunkering of ammonia. MPA will continue to work closely with industry, unions, and research institutes to enhance training of maritime workers.
In July 2024, MPA and the Energy Market Authority (EMA) shortlisted two consortia, Sembcorp-SLNG and Keppel’s Infrastructure Division, in a restricted Request for Proposal (RFP), to advance to the next round of evaluations to provide a low- or zero-carbon ammonia solution on Jurong Island for power generation and bunkering.
Since then, the consortia have proposed two additional ammonia bunkering proposals from Mitsui & Co., Ltd and Fortescue-Equatorial Marine Fuels, which have been evaluated and selected. The two proposals, added to the existing three under the two shortlisted consortia, will be considered in the next round of the RFP process.
The development of multi-fuel bunkering capability in Singapore will help create new job opportunities in related fields, including trading, green technology, sales, legal, and finance.
To support the operationalisation of a higher mix of low-carbon alternative fuels, both EnterpriseSG and MPA are developing the Singapore standards for methanol bunkering and ammonia bunkering by 2024 and 2025 respectively. The standards will cover custody transfer requirements, safety procedures and crew competencies, to ensure safe bunkering operations and handling of these fuels.
Refreshed Maritime Singapore Green Initiative to Encourage Early Adoption of Green Fuels and Technologies
In line with the strengthened global commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from ships, MPA will continue to facilitate global negotiations currently underway at the IMO. MPA has updated various green initiatives and incentives under the Maritime Singapore Green Initiative (MSGI) to encourage early adoption of zero and near-zero emission technologies and fuels. MPA will commit $50 million to support the implementation of the refreshed MSGI. Please refer to Annex A for details.
Maritime Energy Training Facility Attracts New Partners
Dr Amy Khor also announced the onboarding of 29 new Maritime Energy Training Facility (METF) partners from various shipping companies, ship management companies, trading companies, maritime associations and institutes of higher learning. Please refer to Annex B for details. They add to the existing 22 partners. The new partners will collaborate with MPA to validate and shape METF’s training courses, including the training curriculum and curriculum delivery of courses on future fuels and technologies supporting maritime decarbonisation.
The industry’s growing support for METF reflects the strong interest and urgent need for new and enhanced training courses in the maritime sector to address the skills and competency gaps in operating vessels powered by zero or near-zero emissions fuels, such as methanol and ammonia.
The METF courses has trained over 300 personnel since its announcement in April 2024. More facility enhancements will be progressively developed by 2026 and is expected to train more than 10,000 maritime personnel, including seafarers, by the 2030s.
Green and Digital Shipping Corridor (GDSC) Collaborations to Accelerate Decarbonisation and Digitalisation of International Shipping
Singapore-Shandong GDSC
Singapore and Shandong province of the People’s Republic of China have signed the Singapore-Shandong GDSC at the 25th Singapore-Shandong Business Council meeting co-chaired by Minister for Transport and Second Minister for Finance, Chee Hong Tat, and Governor of Shandong Provincial Government, Zhou Naixiang. Shandong is China’s second most populous province after Guangdong, with approximately 101 million people, and the third largest provincial economy in China after Guangdong and Jiangsu with a GDP of 9.2 trillion RMB (approximately 1.7 trillion SGD) and GDP growth of 6% in 2023. Together with the Singapore-Tianjin GDSC, these GDSCs support closer digital and green fuel collaboration between Singapore and the Bohai and Yellow Sea Region.
Singapore - Port of Los Angeles (LA)- Port of Long Beach (LB) GDSC
Three major shipping lines — Hafnia, K-Line, and MOL — are in early discussions to join the LA-LB-Singapore GDSC initiative. Each partner would be expected to spearhead a project to advance the corridor’s decarbonisation and digitalisation goals, such as the adoption of net-zero fuels, Just-in-Time route optimisation, and energy efficiency technologies such as wind-assisted ship propulsion. The addition of the new partners will significantly strengthen the GDSC’s capacity to drive innovation in sustainable shipping practices and accelerate the adoption of zero/near-zero emission fuels and green technologies along the corridor.
Singapore-Port of Rotterdam GDSC
The potential demand for zero or low-emission fuels from all shipping lines within the Singapore-Port of Rotterdam Authority (PoR) GDSC corridor was discussed at the GDSC stakeholder workshop conducted by MPA and the PoR in Rotterdam in September 2024. Based on current order books, there is a potential demand by 2028 for up to five million tonnes per year for greener variants of methane and methanol for more than 200 vessels along the corridor. The ports have also welcomed two new members – GATE Terminal and Singapore LNG Terminal – to the GDSC, to support efforts to develop a pilot trial and regulatory sandbox for bio-methane.
Singapore has entered into GDSC arrangements with Australia, China, Japan, Netherlands, and the United States of America, reflecting the multilateral approach and support for sustainable shipping.
ANNEX A

ANNEX B


source: MPA
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at: