One of the world’s biggest emitters of greenhouse gases, India aims to cut emissions to net zero by 2070, and the shipping minister said three of its ports would initially have bunker facilities for green hydrogen and ammonia. The initial ports in the effort are to be Paradip in the east, Kandla in the west, and Tuticorin in the south. More than 200 ports dot India’s coastline, which stretches 7,500 km (4,660 miles), in addition to the 12 major ones, altogether accounting for 95% of its trade by volume and 65% by value. Authorities want electricity to power at least half the vehicle and equipment needs of major ports by 2030, rather than diesel, and raise that figure further to 90% by 2047.
To meet the net-zero goal, at least 40% of India’s electricity will have to come from renewables. To that end, the new shipping guidelines require ports to satisfy at least 60% of electricity needs through renewables by 2030 and 90% by 2047. Also, by 2030, all ports must achieve cuts of more than a fifth in energy consumption on each tonne of cargo versus 2023, the guidelines show. To boost the use of gas, the shipping ministry wants ports to set up at least one liquefied natural gas (LNG) bunkering station by 2030 and electric vehicle charging stations in and around port areas by 2025.
Alliances for Decarbonization
ABS explores near-shore green hydrogen production in Korea: ABS joined Korean industry leaders in the signing of a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to produce a feasibility study for a near-shore floating platform of green hydrogen production and liquefaction. The study is the latest in ABS’ pioneering work to support green hydrogen production, which includes an approval in principle (AIP) for HD Hyundai Group’s offshore green hydrogen production platform. The Korean government is supporting commercial-scale production of green hydrogen, with the expectation of increasing energy self-efficiency. The feasibility study will be included in a report from the Jeolla Province to determine the viability of developing a green hydrogen production and liquefaction facility at a near-shore floating platform utilizing off-shore wind power.
Port of Newcastle commits to global hydrogen partnership: Port of Newcastle joined forces with ten global energy enablers to commit to the Platform Zero Global Partnership for Hydrogen Innovation – a collaborative global partnership to support hydrogen innovation. With further membership expected in the future, the 10 companies to date who have signed the partnership agreement alongside Port of Newcastle are Port of Rotterdam, HunterNet Newcastle, Newcastle Institute for Energy and Reseources (NIER), Erasmus University Rotterdam, Imperial College of London, Complexo do Pecem, Gemeente Rotterdam and Wicked Acceleration Labs.
Wood teams up with SGN to boost UK hydrogen plans: Consulting and engineering company Wood has announced that it is working with gas distribution company SGN to accelerate plans for key hydrogen transmission infrastructure in Scotland and southern England that supports the UK’s commitment to Net Zero by 2050. Over the next 12 months, Wood said it is delivering three pre-FEED studies to determine the route and design of new dedicated hydrogen pipelines and associated transmission infrastructure, adding that the proposed concept also repurposes existing natural gas infrastructure, which will link hydrogen producers with energy users seeking to use hydrogen to lower their carbon emissions. Projects H2 Caledonia and H2 Connect are involved in the studies.
UK law firm joins Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center: The Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping and UK law firm Allen & Overy have formalized their collaboration by signing a partnership agreement. As disclosed, the partnership agreement was signed today. With this agreement, Allen & Overy becomes a Knowledge Partner to the center, committing to a long-term strategic collaboration and contribution to decarbonizing the maritime industry. By establishing a partnership with Allen & Overy, the center expects to enhance its ability to develop and implement breakthrough decarbonization projects around the world by navigating a diverse and challenging regulatory landscape.
Industry Actions
Philippines and Indonesia spearhead training programs for seafarers as shipping moves toward decarbonization: The Philippines and Indonesia, which are home to just under 21% of the world’s crew members, are taking action to support their seafarers in developing modern skill sets as shipping decarbonizes. The country has been working on the tripartite International Advisory Committee on Global Maritime Affairs (IACGMA) launched in January 2023. The IACGMA’s key aims include providing appropriate training to the country’s seafarers in compliance with the Standards of Training, Certification, and Watchkeeping (STCW) Convention. The IACGMA will also address concerns regarding ambulance-chasing, unfair labour practices, and issues related to the employability of Filipino seafarers overseas. A recent study by DNV has estimated that 800,000 seafarers will require additional training by the mid-2030s to handle the fuels, technologies, and ships of the future.
Next Generation of Vessels
CONTAINER
MSC’s eco-friendly 16,000 TEU boxship aces sea trials: A new Neo Panamax containership, built by Chinese shipbuilder Dalian Shipbuilding for Swiss shipping major MSC, has completed its sea trials. The 16,000 TEU boxship is the first Neo Panamax the Chinese shipbuilder constructed for MSC. The ship has a total length of about 366 meters, a molded width of 51 meters, and a molded depth of 30.2 meters. It can carry more than 16,500 standard containers. It encompasses environmentally friendly, efficient, and energy-saving technologies. According to Dalian, its EEDI is more than 57% lower than the baseline.
Yang Ming is ready to move forward with the acquisition of LNG-powered boxships: Taiwanese shipping company Yang Ming Marine Transport Corporation is set to launch contract negotiations for the construction of five LNG dual-fuel 15,000 TEU-class container carriers. The company said that it was now ready to move to the negotiation stage for the contract signing and construction matters after going through an open and extensive bidding process.
Hudong Zhonghua floats out CMA CGM’s 1st 13,000 TEU dual-fuel boxship: Chinese shipbuilder Hudong-Zhonghua Shipbuilding, a subsidiary of China State Shipbuilding Corporation (CSSC), has launched the first 13,000 TEU containership powered by liquefied natural gas (LNG) for French shipping giant CMA CGM. As informed, the launching took place on 15 May. The ship is the latest generation of green, environment-friendly, high-efficiency and energy-saving container ships in the world. The boxship has a total length of 336 meters and a width of 51 meters. The cargo tank has a capacity of 14,000 cbm. Specifically, the vessel includes GTT’s Mark III containment system. After completion, it will be the largest dual-fuel container ship operating on the South American route, according to the shipbuilder.
MSC sets sights on ammonia dual-fuel ships: Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC) has tapped class society Lloyd’s Register, German engine manufacturer MAN Energy Solutions and Shanghai Merchant Ship Design & Research Institute (SDARI) for a design for the ammonia dual-fuel operation of a future containership. A memorandum of understanding between the parties will see the development of technical specifications and associated design documents for a variant of SDARI’s twin island 8,200 teu boxship design for a vessel contracted to LR class by MSC, which should give the Swiss-based liner giant the option of using ammonia as main propulsion fuel for future newbuilding contracts.
CRUISE
Princess Cruises names second LNG-powered cruise ship: Princess Cruises, an American cruise line owned by Carnival Corporation, has named its second LNG-powered Sphere class cruise ship being built by Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri. This second Sphere class ship was named Star Princess and it will sail an inaugural season of Mediterranean voyages when it debuts in August 2025. At 175,000 tons and carrying 4,300 guests, Star Princess and its sister ship, Sun Princess, are the largest ships ever built for Princess Cruises. The two vessels in the Sphere class will be powered by LNG fuel technology and include advanced sustainable innovations. Princess Cruises and Fincantieri finalized the contracts for the construction of two next-generation 175,000-ton dual-fueled cruise ships back in 2019.
Shipyards
CIMC SOE starts building Seaspan’s second LNG bunkering ship: Chinese shipbuilder CIMC Sinopacific Offshore & Engineering (CIMC SOE) has started building the second 7,600 cubic metre LNG bunkering ship for Canadian shipowner Seaspan. Equipped with two azimuth thrusters and two bow thrusters, this ship design integrates the latest technology, improves the capacity of the power storage system, and further reduces operational pollution emissions and greenhouse gas emissions, CIMC SOE said.
Construction starts on COSCO’s 2nd 700 TEU electric containership: Chinese shipbuilder COSCO Shipping Heavy Industry (Yangzhou) has started the construction of the second 700 TEU electric containership for compatriot COSCO Shipping. As informed, the construction ceremony took place on 8 May in the presence of the shipowner, ship survey authority, maritime department, and shipyard.
Technology
Japanese make ammonia engine breakthroughs: NYK Line, IHI Power Systems, Nihon Shipyard, Japan Engine Corporation, and ClassNK have announced today that the world’s first four-stroke ammonia-fuelled engine has successfully completed a land-based test for the stable combustion of ammonia having an 80% co-firing ratio as part of a demonstration project for the commercialization of vessels equipped with a domestically produced ammonia-fuelled engine. In April this year, IHI Power Systems commenced operational tests at its Ota plant on a 280 mm bore four-stroke ammonia-fuelled marine engine for the main engine of a tug.
Ricardo, sHYpS to develop H2 fuel cell propulsion tech for passenger ships: Ricardo, a strategic, environmental, and engineering consulting company, is working with the Sustainable Hydrogen Powered Shipping (sHYpS) consortium to design and develop hydrogen fuel cell propulsion technologies to power the next generation of zero-emissions passenger ships. According to Ricardo, the project involving 13 partners in six European countries will accelerate the adoption of hydrogen as a renewable fuel in the maritime industry. The work has been funded by UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) under the UK Government’s Horizon Europe funding guarantee.
Fuels
New ICS report pinpoints ‘risk multipliers’ to Maritime’s green transition: The International Chamber of Shipping (ICS), in its new Maritime Barometer Report 2022-2023, has revealed that uncertainty over fuel availability and infrastructure puts at risk ambitions to meet decarbonization targets, reinforcing the need for a clear plan of action to mitigate risk. The report is the first full-scale annual survey of risk. More than 130 C-suite decision makers, half of them shipowners and approximately 35% consisting of ship managers have provided insight into the issues preoccupying them and how they are placed to manage their impact. The aim of this report is to present objective insight into perceived industry risk and confidence, which can be used to inform how the industry – and individual stakeholders within it – respond to key issues. While the practical implications of new greenhouse gas reduction regulations have continued to be the biggest concern for two years in a row, respondents also demonstrated evolving opinions on the fuel landscape. This includes a shift in attitudes towards wind and nuclear power as potential, viable energy sources.
Vopak opens new infrastructure to support sustainable energy production in the port of Rotterdam: Vopak celebrates the opening of 16 new tanks with a combined capacity of 64,000 cubic meters at its Vlaardingen terminal in the port of Rotterdam. The new tanks are designed to store waste-based feedstocks to produce biodiesel and sustainable aviation fuel and will help meet the rising demand for energy from renewable sources in Europe. Vopak Vlaardingen has a long-term commercial agreement with Shell to store the feedstocks for Shell’s new biorefinery in Rotterdam. Shell’s biorefinery will be one of Europe’s largest sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) production facilities, producing SAF and renewable diesel from waste materials such as used cooking oil, waste animal fat, and other residual products. Vopak Terminal Vlaardingen is strategically located in the Port of Rotterdam and is well-connected for logistics via vessels, barges, trucks, and trains. The terminal has extensive experience in storing products such as used cooking oil and tallow.
Forth Ports ramps up decarbonization efforts with 2042 net-zero pledge: UK’s third largest ports group Forth Ports has outlined its commitment and the actions it is taking to achieve a Net Zero carbon operation by 2042. To achieve this across the group’s eight ports, the team is overhauling and electrifying equipment and machinery, switching to low-carbon fuels, increasing on-site renewable energy generation, and promoting low-carbon delivery alternatives such as rail and barge. This is complemented by an investment in new port infrastructure to support the offshore wind revolution taking place in the North Sea. The net-zero plans encompass the use of sustainable electricity, low-carbon fuels, and low-carbon logistics.
Governments
Montenegro inks MoU with US companies for LNG terminal in the port of Bar: The Government of Montenegro is advancing works to install an LNG terminal in the port of Bar as it signs a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with US companies Enerflex Energy Systems and Wethington Energy Innovation. As outlined in the MoU, the LNG terminal would consist of an offloading pier for imports of LNG, storage facilities for LNG, and a regasification facility directing the gas into a short pipeline to the nearby thermopower plant.
Jaxport partners boost the growth of LNG as a clean marine fuel: Jacksonville Port Authority (Jaxport) has facilitated the move of dozens of liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage tanks, owned by LNG supplier Eagle LNG Partners, through the port’s Blount Island Marine Terminal. According to Eagle LNG, half of the tanks will be used to temporarily increase storage at its Jacksonville LNG bunker facility near the Talleyrand Marine Terminal, and the other half will be used for exporting LNG to the Caribbean and elsewhere.
Eagle LNG said the tanks bound for the Caribbean mark the company’s progression toward replacing petroleum with natural gas for power generation to several islands, including Aruba, as well as progress following a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between Aruban leaders and Jaxport to grow business connections.
Ports
Danish duo to establish country’s 1st facility for handling captured CO2: The Port of Aalborg and Fidelis New Energy have entered into an agreement to establish Denmark’s first facility for handling captured CO2. In 2027, Fidelis New Energy will supplement the large facility in Aalborg with additional facilities in Kalundborg. The recipients of the facility will enable the commercial storage of or utilization of CO2 (CCUS). CCUS is set to play a decisive role in the realization of Denmark’s national reduction target towards 2030. The project is the first of its kind in Denmark and Fidelis New Energy’s first in Europe, thus becoming a crucial component for handling European-captured CO2.
By Maria Bertzeletou,
Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com


 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 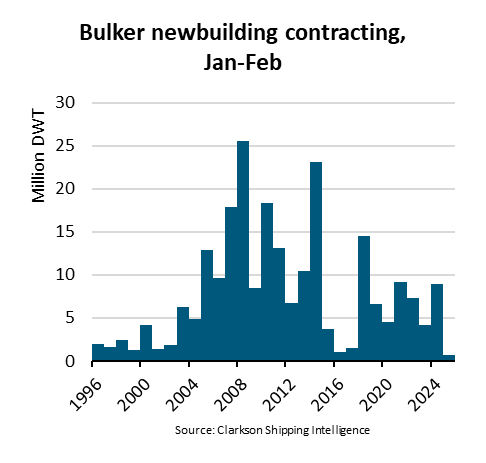 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar