As the maritime industry transitions to a low and zero-carbon future, African maritime players are being advised to implement new training infrastructure for seafarers to adapt to the ongoing continent’s green transition. Speakers at ‘Unlocking Green Maritime Jobs’ panel discussion held on 4 May outlined the growing demand for seafarers able to handle low and zero-carbon fuels (such as hydrogen and ammonia) and new technologies that will be needed to progress towards a decarbonized maritime shipping sector by 2050. Research commissioned by the Maritime Just Transition Task Force found up to 800,000 seafarers could require additional training by the mid-2030s to use these low- to zero-carbon fuels under the possible net-zero target.
There are some noteworthy initiatives already in place. The National Seafarer Development Programme (NSDP), run by the South African International Maritime Institute (SAIMI), and the International Maritime Employers Council (IMEC) is due to launch IMEC South African cadet training program this year, with the first group of 50 cadets starting this month.
Alliances for Decarbonization
IRENA and ThyssenKrupp to collaborate on green hydrogen solutions: The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) has signed a partnership agreement with German company Thyssenkrupp to advance green transformation through green hydrogen solutions. As informed, the partners signed the agreement in pursuit of global development and Paris Agreement goals. Under the agreement, both organizations will work together and share knowledge on the large-scale production and supply of green hydrogen and other green energy carriers and their transport. This includes the entire hydrogen value chain in demand, supply, and infrastructure.
MariApps and zero44 announce a partnership to enable shipping companies to comply with the EU Emissions Trading System: zero44, a digital solutions provider focused on carbon regulation, and MariApps Marine Solutions, one of the leading providers of digital solution suites for the maritime industry, announced a partnership to support their customers with the EU Emission Trading System (EU ETS). Together, the two companies will offer a one-stop-shop solution for EU ETS for the maritime sector – starting from MariApps’ established performance optimization, data collection, and reporting overviews all the way through to compliance processes, stakeholder alignment, Union Registry management, and trading access provided by zero44.
Prominent maritime ports, academia & innovation hubs unite to accelerate hydrogen innovation: Prominent maritime ports, universities, and innovation hubs from Australia, Brazil, Chile, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands have joined forces in a ground-breaking initiative aimed at expediting innovation for green hydrogen. Named the Platform Zero Global Partnership for Hydrogen Innovation, the initiative is a collaborative global partnership aimed at supporting hydrogen innovation. Representatives of 14 organizations, innovation hubs, and universities constituting the partnership signed a Memorandum of Understanding on May 9, in Rotterdam, under the supervision of the Dutch Minister for Foreign Trade and Development, Ms. Liesje Schreinemacher, to accelerate the renewable energy transition with Platform Zero, Port of Rotterdam, and the City of Rotterdam.
Industry Actions
Norwegians press ahead with pioneering ammonia-fuelled dry bulk project: Skarv Shipping Solutions, a joint venture between Peak Group and Grieg looking to pioneer green short-sea dry bulk trades, has received NOK130m from the Norwegian government fund, Enova, to help it acquire three ships for use along the Norwegian coast. The 4,000 dwt vessels will potentially reduce emissions by up to 90% compared to traditional vessels, thanks to innovative technologies like batteries, ammonia engines, rotor sails, and energy-efficient hull design. The engines, likely to be supplied by Wärtsilä, will be among the world’s first four-stroke ammonia engines.
Höegh Autoliners taps North Ammonia to power its dual-fuel car carriers: Norwegian shipowner Höegh Autoliners has signed a partnership agreement with compatriot green energy provider North Ammonia for the supply, distribution, delivery, and consumption of green ammonia. As disclosed, partnering with North Ammonia marks another sustainability milestone for Höegh Autoliners and is an important step on the path to zero. The green ammonia is meant for ammonia-ready dual-fuel Aurora-class vessels. Securing the supply and delivery of green ammonia from North Ammonia’s planned production facility in Arendal in southern Norway will help the firm source green ammonia.
Classification
ABS and partners looking into near-shore green hydrogen production in Korea: The MoU was signed by ABS, the Korea Institute of Energy Technology (KENTECH), HD Korea Shipbuilding and Offshore Engineering (HD KSOE), part of HD Hyundai Group, Linde Korea, and Linde PLC. According to the classification society, the study is the latest in its work to support green hydrogen production, which includes an approval in principle (AIP) for HD Hyundai Group’s offshore green hydrogen production platform. The feasibility study will be included in a report from the Jeolla Province to determine the viability of developing a green hydrogen production and liquefaction facility at a near-shore floating platform utilizing offshore wind power.
Next Generation of Vessels
BULKER
EPS’ newbuild LNG dual-fuel bulker named in China: A newbuild 210,000 dwt LNG dual-fuel bulk carrier built for Singapore-based shipowner Eastern Pacific Shipping (EPS) has been named at Chinese shipyard New Times Shipbuilding (NTS). The vessel was named Mount Tai during a ceremony held on 4 May at the Chinese shipyard. Following the naming ceremony, Mount Tai is expected to be delivered and put into operation by the end of this month, NTS said. The shipbuilder noted that Eastern Pacific Shipping has currently on order four 110,000-ton oil tankers, eleven 210,000-ton dual-fuel power bulk carriers, and seven 7,000 TEU container ships.
TANKER
International Seaways expands fleet with 2nd LNG-fueled supertanker chartered by Shell: The 300,000 dwt vessel, named Seaways Enterprise, was delivered in April 2023, a month after the delivery of the first vessel from the batch, Seaways Endeavor. International Seaways has one more dual-fuel vessel under construction at DSME and it is expected to deliver in the second quarter of 2023. Each vessel is employed on a long-term time charter with oil major Shell and is financed under a sale and leaseback arrangement with a fixed interest rate of approximately 425 bps. The three LNG-powered VLCCs were ordered in 2021.
HGK Shipping signs MoU on hydrogen tech, christens new chemical tankers: HGK Shipping, Hydrogenious LOHC Maritime, and Hydrogenious LOHC Technologies have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the goal to develop a scalable solution to make hydrogen available as a source of energy on a large scale. According to HGK, the technology is based on hydrogen, which is bound in a liquid carrier (LOHC – liquid organic hydrogen carrier). The plan is to develop a demonstration vessel by 2028 and then put it into service, HGK said, adding it will be possible to propel the ship with a fuel cell, which is fed with energy from the hydrogen released from the LOHC. In addition to the MoU signing, HGK also held a naming ceremony for two newbuildings.
GTT, SWS get BV’s nod for LNG dual-fuel VLCC design: French LNG containment specialist GTT and Chinese shipbuilder Shanghai Waigaiqiao Shipyard (SWS) have obtained approval in principle from classification society Bureau Veritas (BV) for the design of LNG dual-fuel very large crude carrier. This approval is part of a joint development project (JDP), started by the partners in May 2022. SWS has designed the vessel with optimized hull lines and equipped with GTT’s high-technology system for LNG cargo containment, to enable safe and flexible carbon-neutral shipping. The operational flexibility offered by this new 10,000 cbm capacity fuel tank concept allows ship owners and charterers to make round-trip voyages between the Middle East, Asia, and Europe with a single LNG bunkering operation, according to the company.
CONTAINER
Hudong Zhonghua cuts steel for CMA CGM’s 6th dual-fuel boxship: Chinese shipyard Hudong-Zhonghua Shipbuilding has cut steel for the sixth and final dual-fuel LNG powered 13,000TEU dual-fuel container ships being constructed for France’s CMA CGM. These vessels are designed to operate using either traditional fuel or liquefied natural gas (LNG). The 336-metre long and 51-metre wide ship will be equipped with a 14,000 cbm MARK III LNG cargo tank and will be able to load 2,400 containers with a maximum capacity of 13,2000 TEUs. It will also feature flexible container loading technology and use energy-saving ducts, rudder balls and other devices for improving its performance.
RO RO
Construction of Stena Line’s methanol-ready NewMax hybrid duo about to begin: The company said that the construction of the NewMax vessels will begin shortly with the launch of operations on the Irish Sea expected in 2025. China Merchants Jinling Shipyard in Weihai, China has been entrusted with the construction process through Stena RoRo and both ships.
The ships are intended for the Belfast-Heysham route and add 80% capacity as the company responds to increasing customer demand for capacity and sustainability performance. The ships will be operating from Stena Line’s port in Belfast. Stena Line added it was currently working closely with the supply chain of methanol and has secured future volumes of e-methanol to fulfill its strategic ambition of shifting to renewable fuels and cutting 30% of its CO2 emissions by 2030. The company is already operating a ferry on methanol, the Stena Germanica, which was converted back in 2015.
CRUISE SHIPS / FERRIES
LNG-powered Icon of the Seas gearing up for sea trials: Icon of the Seas, Royal Caribbean International’s first LNG-powered cruise vessel, is scheduled to commence sea trials in mid-June. According to Meyer Turku, the shipbuilder of what is expected to be the world’s largest and most technically advanced cruise ship, the construction is progressing at a good pace and preparations for her sea trials have already started. The Finnish shipbuilder started construction on the Icon of the Seas in June 2021 and installed an LNG fuel tank in November 2021. The ship was launched on 9 December 2022 and moved to the outfitting dock. Icon of the Seas is Royal Caribbean’s first ship that runs on LNG and utilizes fuel cell technology. The vessel will also feature shore power connections and waste heat recovery systems. Furthermore, it will have air lubrication of the underwater hull, sending millions of microscopic bubbles along the hull of the ship to reduce friction.
Brittany Ferries unveils the name of its new LNG-battery hybrid ferry: Brittany Ferries has revealed the name of its forthcoming ship, which will be able to run on liquefied natural gas (LNG), on battery power, or on a combination of the two in hybrid mode. As disclosed, the new eco-friendly ferry will be named Guillaume de Normandie. The ship is planned to join the company’s fleet in May 2025, sailing alongside its sister ship Saint-Malo. The ferry will also be the fourth vessel in the fleet to be fuelled by LNG. It will be powered by two 13,740 kW engines. The vessel will switch to LNG-electric and full-electric mode mainly on the approach to harbors and at the quay. Preliminary studies suggest a fuel consumption reduction of up to 9 percent when in service, thanks to her hybrid technology, according to the company. Moreover, the ship will also be plug-in ready, meaning zero emissions when alongside. The aim in Caen is to have shore-side power in place by 2027 thanks to investment by the Normandy region and Ports de Normandie.
Shipyards
Hudong-Zhonghua builds 4th LNG carrier for CSSC Shipping: According to the shipbuilder, the undocking ceremony for the ship with the working name H1830A took place on 4 May. The LNG carrier has a total length of 295 metres, a width of 45 metres and a depth of 26.25 metres. It belongs to the company’s LNG ship type of the X-DF series. These vessels are propelled by dual-fuel low-speed diesel engines and equipped with advanced environmental protection devices, the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) devices. The ship is designed to meet the most stringent emission standards of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the IMO TIER III environmental protection requirements.
South Korean shipbuilder HJ Shipbuilding & Construction HJSC rolls out new LR-approved LNG bunkering vessel design: South Korean shipbuilder HJ Shipbuilding & Construction (HJSC, formerly Hanjin Heavy Industries & Construction) has developed a new LNG bunkering vessel for which it also obtained approval in principle (AiP) from classification society Lloyd’s Register (LR). The new 7,500 cbm LNG bunkering vessel follows the delivery of 5,200 cbm bunkering vessel, Engie Zeebrugge to Japanese shipping company NYK in 2017. In late 2020, the vessel was renamed Green Zeebrugge and in 2021, it was chartered to the Dutch company Titan. The new vessel was designed for ship-to-ship operations and is equipped with two independent pressure-type LNG tanks certified by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to supply 7,500 cbm of LNG at once.
Technology
Air Products’ technology and equipment selected for the Chinese electric-driven LNG project: Industrial gases company Air Products has signed an agreement to supply its proprietary LNG process technology and equipment to French engineering company Technip Energies for an electric-driven LNG project in China. Last month, Technip Energies was selected by Shaanxi Yanchang Petroleum Group and Shaanxi Gas Group to provide the process design package (PDP) and front-end engineering and design (FEED) work for the 3 million cubic metres per day Xi’An LNG Emergency Reserve & Peak Regulation project in China. The deal also included the supply of key equipment for a single 0.8 million ton per annum (mtpa) LNG train.
Fuels
AMMONIA
EPS, Jiangnan ink deal for construction of world’s largest ammonia carriers: Jiangnan Shipbuilding, a subsidiary of China State Shipbuilding Corporation (CSSC), has signed a contract with Singaporean shipping company Eastern Pacific Shipping (EPS) for the construction of four Very Large Ammonia Carriers (VLAC) with a capacity of 93,000 cubic meters. The Chinese shipbuilder said that based on their capacity these will be the largest ammonia carriers in the world. This type of vessel is the preferred option for transporting green ammonia over long distances, but it can also be fully loaded with liquefied petroleum gases, such as propane and butane.
Aker Horizons and VNG ink LOI to ship ammonia from Norway to Germany: Norway-based green energy developer Aker Horizons and German gas group VNG have signed a letter of intent (LOI) aiming to ship green ammonia from Narvik, Northern Norway, to Germany. VNG said it plans to procure up to 200,000 tonnes of green ammonia per year from Aker Horizons’ large-scale green industrial hub under development in Narvik as of 2028. The green ammonia will be shipped from Narvik to terminals in Germany, where VNG will distribute it further as ammonia or hydrogen to its customers, who will use it to decarbonize their operations. The LOI is a first step towards a firm supply agreement between the parties and could be expanded to further areas of collaboration.
Hyphen and Koole Terminals team up on green ammonia supply: Hyphen Hydrogen Energy, a green hydrogen development company, and Koole Terminals, an independent provider of integrated services for storage, processing, and logistics, have signed a Letter of Intent (LoI) on green ammonia. The LoI covers the import of green ammonia into north-western Europe with Hyphen planning to supply its customers using the import terminal being developed by Koole Terminals, located in the Port of Rotterdam, Netherlands. Hyphen said it is targeting annual production of one million tonnes of green ammonia to come online by the end of 2027, expanding to two million tonnes of green ammonia by 2029. Over the past year, it has signed Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) with several potential European customers, targeting the supply of up to 750,000 tonnes of green ammonia annually.
LNG
Kanfer and CB Fenton bring in a new partner to commercialize LNG bunkering hub in Panama: Norwegian company Kanfer Shipping and CB Fenton, part of Ultramar (Chile), have signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Melones Oil Terminal (MOTI) to commercialize small-scale LNG bunkering and distribution in Panama. In December 2022, Kanfer Shipping and CB Fenton joined forces to set up a hub for LNG bunkering and small-scale LNG distribution in/out of Panama. Now, the companies are bringing onboard MOTI, one of the largest marine fuel oil terminal operators in Panama which provides marine fuels storage services, and its affiliate company Trader Tankers to commercialize the LNG bunkering hub in Panama and more specifically in Balboa. The parties see LNG as the transition fuel for the maritime industry and consider Panama a strategic location for LNG bunkering.
Biofuels
Japan sees the start of a continuous supply of biofuel for ships on a commercial basis: Toyota Tsusho Corporation and Toyotsu Energy Corporation have launched Japan’s first continuous supply of biodiesel blended fuel (biofuel) on a commercial basis to ships operated by Toyofuji Shipping Co., Ltd. at the Port of Nagoya. According to Toyota Tsusho, the launch follows repeated biofuel supply trials for ships that the company conducted at the Port of Nagoya, as well as studies into its effectiveness and practical application. Toyota Tsusho conducted its first biofuel operation trial at the Port of Singapore in April 2021, and since then, it said it has conducted verification tests for the commercialization of biofuel, such as its effectiveness and supply operations, including biofuel supply trials at the Port of Nagoya from April 2022 using ship-to-ship bunkering, a method of fueling tugboats and coastal trading vessels operating within the port by a fuel supply ship sideways.
Inpex and Astomos to supply Middle East’s first-ever marine biofuel for VLGC: Japanese LPG trader and importer Astomos Energy Corporation and compatriot energy company Inpex Corporation have reached an agreement to supply B24 biofuel bunker to a very large gas carrier (VLGC) in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The agreement will see Inpex supply B2 biofuel to the VLGC chartered by Astomos through a bunker vessel operated by oil and shipping company Monjasa at Khor Fakkan port in the UAE emirate of Sharjah. The partners pointed out that this will be the first instance in which biofuel is supplied to a VLGC in the Middle East. B24 biofuel consists of 24% fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) and 76% very low sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO), a conventional bunker fuel. Dubai-based Neutral Fuels will produce the FAME from waste cooking oil collected from restaurants and hotels in the UAE and Monjasa will supply the VLSFO and blend it with the FAME.
Ports
Port of Oakland, CalSTA, and Japan to cooperate on green seaport initiatives: The Port of Oakland and the California State Transportation Agency (CalSTA) have met with a delegation of Japanese Ministry officials to discuss green initiatives to reach zero emissions from seaport operations. The meeting was a follow-up to a clean energy trade mission to Japan in March where California policymakers, decisionmakers, and business executives met to exchange ideas about tackling climate change. Furthermore, they discussed growing green energy and creating new investment and trade opportunities. This time, as a major U.S. West Coast seaport, Port of Oakland officials were part of the California delegation and discussions. The discussions were held last week. Japan’s Director General of Ports and Harbor Bureau of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, talked about his country’s efforts to create Carbon Neutral Ports. Japan’s goal is to reach carbon-neutral port operations by 2050.
Carbon removal system to be installed at Port of Los Angeles: Captura, a carbon removal company founded at Caltech, has partnered with AltaSea at the Port of Los Angeles to install its newest ocean carbon removal system. The latest system is a 100x scale-up from the company’s first pilot that has been operating at Newport Beach, California since August 2022. It will be able to capture 100 tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the ocean annually. The system was funded by a third Californian company, Southern California Gas Company (SoCalGas), as part of an ongoing relationship with Captura to support the demonstration and scale-up of the technology. Captura will use AltaSea’s campus as the site for technology testing, research, and analysis to validate, scale and improve its Direct Ocean Capture (DOC) technology.
Gidara Energy gets the green light for a methanol plant in port of Amsterdam: Gidara Energy has received a key environmental permit for its renewable methanol facility to be built at BioPark in the port of Amsterdam. The environmental permit was granted by the province of Noord-Holland, allowing the company to build its Advanced Methanol Amsterdam (AMA) facility. Obtaining this permit is a major milestone in the development of the facility, enabling the production of renewable fuels and, in the future, high-quality circular chemicals, Gidara stated.
Ports of Rotterdam and Pecém bolster green hydrogen ties: A new partnership to strengthen bilateral cooperation between the Netherlands and Brazil in port-related energy projects, such as offshore wind energy and green hydrogen production, has been formed. Specifically, 27 parties operating in the ports of Rotterdam and Brazil’s Pecém signed a cooperation agreement on 10 May. In addition to port-related energy projects, the agreement covers port development, logistics, and hinterland connection.
India charts the path toward bunkering of green hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol: India’s Minister for Ports, Shipping, and Waterways, Sarbananda Sonowal, introduced on Wednesday the ‘Harit Sagar’ Green Port Guidelines during a ceremony in New Delhi. The launch of these guidelines marks a significant milestone in India’s journey towards achieving its Zero Carbon Emission Goal by 2070, as outlined by the ministry. The Harit Sagar Guidelines – 2023 embody a holistic approach to port development, operations, and maintenance, emphasizing the concept of ‘Working with Nature’ and minimizing the impact on the harbor ecosystem’s biotic components. The guidelines strongly emphasize the adoption of clean and green energy sources in port operations, while also focusing on the development of storage, handling, and bunkering capabilities for environmentally friendly fuels such as green hydrogen, green ammonia, and green methanol or ethanol.
Governments
Biden administration unlocks $4 billion for electrification of US ports: As disclosed, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) will invest $3 billion to fund zero-emission port equipment and technology and to help ports develop climate action plans to reduce air pollutants, improve air quality and public health in neighboring communities, and advance environmental justice. EPA will also spend another $1 billion to reduce emissions from heavy-duty commercial vehicles, including those that travel in and out of ports. US President Joe Biden has earlier secured $17 billion in investments through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to improve the country’s ports and waterways. The Inflation Reduction Act includes another $4 billion with a focus on electrifying port equipment and heavy-duty vehicles.
By Maria Bertzeletou,
Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com


 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 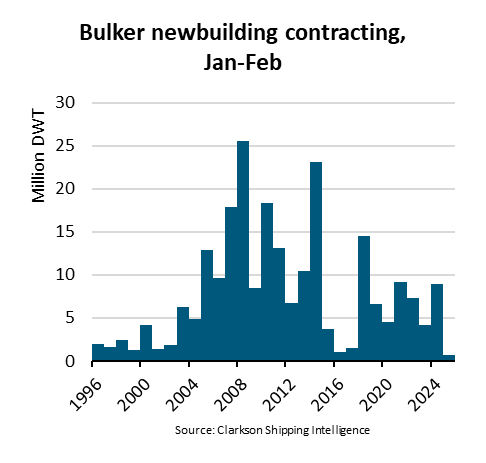 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar