LNG-powered Sun Princess hits the water at Fincantieri: Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri has launched Sun Princess at its yard in Monfalcone, the first of two LNG-powered cruise ships being built for Princess Cruises, an American cruise line owned by Carnival Corporation. With 175,500 gross tons, Sun Princess is the largest ship built in Italy so far, as well as the first dual-fuel ship powered mainly by LNG to enter the Princess fleet. With a capacity of 4,000m3, the vessel is expected to be able to run on LNG for almost 9 days sailing at service speed. The secondary fuel is marine gas oil so no heavy or intermediate fuel oil will be carried on board. The vessel will be outfitted with two shore power connections, on both the port and starboard side of the vessel to enable the ship to turn off the engines and connect to local electric power to run all onboard services during day-long calls in various ports.
GSI delivers first battery-hybrid ferry to P&O Ferries: China’s Guangzhou Shipyard International (GSI) has delivered the first out of two new battery-hybrid ferries to British ferry operator P&O Cruises. As informed, the delivery ceremony took place on 28 February. After the delivery, the ship will be put into operation in the English Channel, mainly traveling between the port of Dover in the UK and the port of Calais in France.
FlagshipONE to use Siemens Energy technology for e-fuel production: FlagshipONE plant, expected to be Europe’s largest commercial production facility for carbon-neutral marine fuels, will use a technology package from German company Siemens Energy. The package comprises four proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysers with a total capacity of 70 megawatts (MW), as well as the plant-wide electrification and automation systems, including innovative digitalization solutions (such as the use of digital twins), and the entire power distribution and compressor systems. The plant, being built in the Swedish coastal town of Örnsköldsvik by Danish energy company Ørsted, is expected to produce up to 50,000 metric tonnes of e-methanol per year from renewable energy and biogenic carbon dioxide from 2025. According to Siemens Energy, Ørsted’s plant represents the start of commercial production of carbon-neutral e-methanol in Europe and will act as a blueprint that can be scaled and replicated at other locations, in Sweden and elsewhere.

Wärtsilä receives 1st order for CCS-ready scrubber systems: Finnish technology group Wärtsilä has received its first order for carbon capture and storage (CCS)-ready scrubber systems. As disclosed, four 8,200 TEU container vessels being built at an undisclosed Asian yard will be fitted with Wärtsilä’s CCS-Ready 35MW scrubber in an open loop configuration. The scrubbers are termed CCS-Ready because, as part of their installation, Wärtsilä will perform additional design and engineering work to ensure that future retrofits for a full CCS system on the vessels have already been accounted for during the newbuilding construction stage. The firm will take measures to ensure adequate space for the future installation of CCS system, incorporate considerations for minimizing idle load and optimizing utilities, and prepare the control and automation system accordingly.
New range of injection systems for low-carbon fuels in the making: Woodward, an engine injection system manufacturer, is developing a new range of injection systems to support the ongoing transition to new fuels in the global energy industry. According to Woodward, the comprehensive portfolio of new systems will be applicable for new and future fuel-powered engines including methanol and ammonia. Designed to support the transition, the systems for power-to-X (P2X) fuels in large engines will range from 100 kW/Cylinder to over 1000 kW/Cylinder to enable all possible combustion concepts. For applications that require the highest levels of power density and efficiency, Woodward said it is developing a high-pressure dual-fuel (HPDF) platform for methanol and ammonia injection with full diesel backup capability.
MOL and Vale to install Norsepower rotor sails on bulker: The two companies have announced a partnership to install rotor sails to a 200,000 tonne bulk carrier employed on a mid-term transportation contract with Vale. The vessel will be fitted with two 35 m x 5 m rotor sails produced by Norsepower. Norsepower’s rotor sails are expected to result in 6 – 10% fuel and GHG emissions savings for the vessel, combined with optimization technology. The installation of the rotor sails is expected in the first half of 2024.
CO2 Storage
Five companies in line for carbon storage acreage in Norway’s waters: The Norwegian Ministry of Petroleum and Energy has received applications from five companies seeking permits related to the injection and storage of CO2 on the Norwegian continental shelf (NCS). The area is located in the North Sea and was announced on 11 January in accordance with the storage regulations. The Norwegian ministry reported that it had received applications from five companies by the time the application deadline expired on 22 February. The companies that have applied for the acreage are Equinor, Neptune Energy Norway, Storegga Norge, Sval Energi, and Wintershall Dea Norge. The ministry is now set to process the received applications with an aim to allocate land according to the storage regulations during the first half of the year.
Fuels
GTT wins ClassNK approvals for innovations in alternative fuels technology: Japanese classification society ClassNK has issued four Approvals in Principle (AiPs) to French LNG containment specialist GTT recognizing the company’s latest development projects in alternative fuels. ClassNK said that it had carried out the verification of these accomplishments in line with its rules including Part N incorporating the IGC Code, Part GF incorporating the IGF Code, and its Guidelines for Ships Using Alternative Fuels. Among the above, the AiP for Recycool™ marked the world-first AiP for a system of its kind.
URBAS and AECOM team up for green and sustainable fuels projects: Spain-based URBAS, specialized in sustainable infrastructures and buildings, real estate development, and renewable energies, has signed an agreement with US-based AECOM, an engineering, architecture, and sustainability company, to develop green hydrogen, green ammonia, and sustainable fuels projects that support the global energy transition.
Through this agreement, URBAS and AECOM said they will work to identify joint business opportunities and offer competitive integrated solutions on an international scale in hydrogen production and transformation projects, as well as the generation of synthetic and sustainable fuels, with a special focus on green methanol projects in Spain.
LNG
Avenir LNG and SSES bunker ZIM’s first LNG-fueled boxship: UK-based small-scale LNG company Avenir LNG and Shanghai SIPG Energy Service (SSES), a subsidiary of Shanghai International Port Group (SIPG), have delivered LNG to ZIM Integrated Shipping Services’ first LNG-fueled containership. According to Avenir, the 15,000 TEU ZIM Sammy Ofer was bunkered with LNG on 2 March 2023 at Yangshan Port. The operation was carried out by SSES’ 20,000 cbm bunkering vessel Hai Gang Wei Lai. The vessel is the first of ten ships ordered by Seaspan as part of a long-term mutual chartering agreement with ZIM Integrated Shipping Services. The deliveries of the remaining nine containerships are anticipated to begin in the first half of 2023.

Shell to supply LNG for Hapag-Lloyd newbuilds: Shell Western LNG has reached a multi-year liquefied natural gas (LNG) supply agreement with German shipping firm Hapag-Lloyd to support marine fuel decarbonization. Under the agreement, Shell will deliver LNG to Hapag-Lloyd’s new ultra-large dual-fuel boxships, which will each have a capacity of more than 23,500 twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs).
The company plans to begin bunkering for the 12 new vessels during the second half of the year. The vessels will receive the LNG at the Port of Rotterdam in the Netherlands. They will operate on the Europe-Far East route and call at major ports, including Rotterdam, the Netherlands; Hamburg, Germany; Singapore; and Shanghai, China. LNG usage is expected to help Hapag-Lloyd instantly lower the CO₂ intensity of the vessels by up to 23% compared to conventional fuels. It is also said to almost eliminate particle emissions entirely.
Methanol
Methanol boxship orders growing more rapidly than all other fuel types: The container segment is leading shipping to new green pastures, taking a massive lead when it comes to investing in methanol propulsion.
According to Alphaliner, methanol boxship orders have grown more rapidly than LNG in the last six months, while carriers have all but ditched orders for conventional fuel oil tonnage with just 8% of orders by capacity so far this year going for the old fashioned bunker fuel. LNG and methanol dual-fuel tonnage now represent 40% of the container orderbook. It is the speed with which methanol has been embraced which has caught the eye. The methanol-fuelled boxship orderbook now stands at 68 ships of 0.93m teu. The segment now represents 12% of the orderbook by capacity, versus less than 1% a year ago.
Methanex and MOL complete first-ever net-zero voyage fuelled by bio-methanol: Methanex Corporation (Methanex) and Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. (MOL) are pleased to announce the dual-fuel vessel “Cajun Sun” successfully completed the first-ever net-zero voyage fuelled by bio-methanol. The voyage is an example of how Methanex and MOL are collaborating to demonstrate the viability of methanol as a marine fuel with a pathway to net-zero emissions. The Cajun Sun, operated by Methanex’s subsidiary Waterfront Shipping and chartered from MOL, departed from Geismar, U.S. on January 17 and arrived in Antwerp, Belgium on February 4. By blending ISCC-certified bio-methanol that has negative carbon intensity with natural gas-based methanol, net-zero greenhouse gas emissions on a lifecycle basis were achieved for the 18-day trans-Atlantic voyage. This innovative fuel solution offers shipping companies the ability to achieve net-zero carbon emissions today, supporting the industry’s transition to a low-carbon future.
Biofuels
IINO trials BP’s marine biofuel on its chemical tanker in Singapore: Tokyo-based shipping company IINO Kaiun Kaisha has conducted a trial on one of its chemical tankers using a marine biofuel blend delivered by British oil and gas company BP in Singapore. On 18 December 2022, IINO’s chemical tanker Chemroad Echo was supplied with B24 marine biofuel, consisting of 24% fatty acid methyl easter (FAME), blended with very low sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO). According to IINO, the FAME component of the marine biofuel blend used in this trial led to a reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the voyage on a lifecycle, well-to-wake approach. Biofuel blends are described as particularly helpful as a “drop-in” solution available to existing fleets without the need for modifications to the engine or infrastructure in most applications.
Marine biofuel demonstration on LPG carrier completed: Astomos Energy Corporation (Astomos) and NYK Line have completed a pilot on the liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) carrier Lycaste Peace (owned by NYK Line and chartered by Astomos), bunkering FAME B24* marine biofuel in Singapore. The test voyage was completed on February 26. The demonstration is part of a project to establish an assurance framework for the supply chain of sustainable biofuels led by the Global Centre for Maritime Decarbonization (GCMD), a non-profit organization in Singapore that aims to support the decarbonization of the shipping industry. In this demonstration test, Astomos and NYK Line, together with the biofuel bunker supplier, proved that the sustainable biofuels in this case are traceable along the supply chain, by tracking the transportation of biofuel from the place of production to Singapore, blending the biofuel with conventional fuels, the site of bunkering, and management of the blended fuels.

Peninsula starts supplying biofuels in the Strait of Gibraltar: Marine fuel supplier Peninsula is commencing the supply of biofuels at its hub ports in the Strait of Gibraltar as part of its strategy to meet increased complexity in the marine fuel mix. Peninsula has recently received a permit from ISCC – International Sustainability and Carbon Certification related to physical supply operations in Gibraltar, Algeciras and nearby ports. According to the company, the ISCC permits the supply of biofuels from feedstocks that have fully traceable, sustainable, and GHG-reducing supply chains, which enables Peninsula to directly support customers seeking drop-in biofuel solutions to help lower their carbon emissions.
Ports
Ports of Los Angeles, and Gothenburg strengthen ties on digitalization and decarbonization: Officials from two of the world’s busiest ports, the Port of Los Angeles and the Port of Gothenburg, Sweden, have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to strengthen their cooperation in a range of areas including sustainability, digital and physical infrastructure, and potential trade opportunities. The MOU was signed at a ceremony held at the Port of Los Angeles last week. The Port of Los Angeles’ Executive Director, Gene Seroka, emphasized the importance of the partnership in his statement, saying that the ports must work together to modernize, innovate, and share best practices due to their pivotal role in the global economy. The MOU builds on an already strong relationship and a shared pursuit of excellence in all aspects of port operations. The two ports will also collaborate on alternative fuels, as well as on strategies to incorporate new and emerging green technologies to minimize the impact of port operations on local communities and the overall environment.
Port of Rotterdam: €3 bln invested in energy transition projects in 2022: Port of Rotterdam has seen several investments in energy transition projects in 2022 worth a total of approximately € 3 billion. Some of these projects include investments in a major biorefinery and Europe’s largest green-hydrogen plant. In July 2022 subsidiaries of Shell have taken the final investment decision (FID) to build Holland Hydrogen I, which will be Europe’s largest renewable hydrogen plant once operational in 2025. The role played by the Port Authority in the planned projects varies from project to project. However, the port has been particularly important in the development of infrastructure that allows companies to operate more sustainably.
ABP rolls out £2 billion green growth and decarbonization plan: Associated British Ports (ABP), the UK’s leading ports group, has launched its wide-ranging new sustainability strategy, Ready for Tomorrow (RFT), backed by a plan to invest around £2 billion in decarbonizing its own operations by 2040. As disclosed, Ready for Tomorrow looks both internally at ABP’s own operations and outwards, to building greater partnership and collaboration to meet the challenges and grasp the generational opportunities of sustainability. For ABP’s own operations, the plan identifies five focus areas for action: Net Zero, air quality, biodiversity, waste, and water management. Each focus area has a program of action plans – including action ideas from ABP’s employees in our ports and other locations – to achieve ambitious but credible targets. This includes a commitment to reach Net Zero from ABP’s own operations (Scopes 1 and 2) by 2040.
Governments
Germany joins Zero-Emission Shipping Mission to spur decarbonization drive: Germany has joined the Zero-Emission Shipping Mission as the new support member to accelerate its decarbonization drive. By joining the Mission, Germany acknowledges the importance of decarbonization of the maritime sector and recognizes the goals as a key lever in the pathway to net zero. The Mission is co-led by Denmark (Ministry of Industry, Business and Financial Affairs, Ministry of Climate, Energy and Utilities and Ministry of Foreign Affairs), Norway (Ministry of Climate and Environment), The United States (U.S. Department of Energy) as well as Global Maritime Forum (representing the Getting to Zero Coalition), and Mærsk McKinney Møller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping.
Green Corridors
U.S. and Fiji working on establishing green shipping corridor: The United States of America, the Republic of Fiji, and the Pacific Blue Shipping Partnership have announced the intent to engage in technical cooperation to help facilitate the establishment of a green shipping corridor. Together, they intend to undertake a feasibility study to explore the potential of creating a green shipping corridor in the region, which can work to expand access to new fuels and technologies. Upon its completion, the partners will initiate discussions on the next steps among key stakeholders. With this announcement, Fiji is also joining the Green Shipping Challenge, an initiative that catalyzes actions from countries and non-state actors to advance the transition to a 1.5-aligned shipping sector.

The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com
















 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 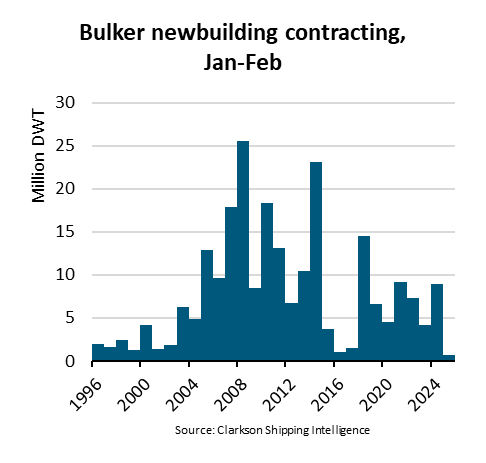 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar