Additionally, these companies will jointly evaluate the performance of an Aquarius Marine Solar Power system that will be supplied by EMP and is currently being installed onboard a ship in their fleet. Several maritime technology providers will also support the study including Furukawa Battery & KEI System. Namely, this would underly potential installation of solar panels on hatch covers of the bulker.
Tsuneishi taps MAN ES to provide a methanol-fuelled engine for the bulk carrier: MAN Energy Solutions (MAN ES), through its licensee Mitsui E&S Machinery, has signed a contract with Chinese shipbuilder Tsuneishi Shipbuilding to provide a methanol-powered engine for a 65,700 dwt bulk carrier. As informed, the company will provide its MAN B&W 6G50ME-LGIM engine. The vessel represents the latest methanol-fuelled engine ordered by the bulk-carrier segment in recent weeks. MAN Energy Solutions developed the ME-LGIM dual-fuel engine for operation on methanol, as well as conventional fuel. The engine is based on the company’s ME-series, with its approximately 8,500 engines in service, and works according to the diesel principle. When operating on green methanol, the engine offers carbon-neutral propulsion for large merchant-marine vessels.

Classification
RINA, ABB to collaborate on decarbonization projects: Classification society RINA has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Swiss-based technology developer ABB with the aim to develop new concepts to reduce emissions in shipping for various vessel types. The collaboration will include the development of commercially viable solutions, including fuel cell systems with carbon capture, to move the shipping industry forward with decarbonization. It further focuses on promoting the use of hydrogen, and the introduction of modern approaches to ship propulsion. As the classification society and third-party certification provider, RINA’s role within the agreement will be to work on providing Approval in Principle (AiP) of design concepts that match the technologies available from ABB and the applicable rules and regulations, along with project and type approvals.
ABS to class UC San Diego’s hydrogen-powered research ship: American classification society ABS has revealed that it will class a hydrogen-fueled research vessel commissioned by the University of California San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography. Designed by Glosten, the vessel will feature a new hydrogen-hybrid propulsion system that integrates hydrogen fuel cells alongside a conventional diesel-electric power plant, enabling zero-emission operations. The design is scaled so the ship will be able to operate 75 percent of its missions entirely using hydrogen. For longer missions, extra power will be provided by diesel generators. The 45.7-meter-long vessel will be equipped with advanced instruments and sensing systems, along with new laboratories, enabling multidisciplinary research, and advancing understanding of the physical and biological processes active in California’s coastal oceans.
Fuels
PBBM supports AboitizPower and JERA push for greener fuels in the Philippines: Aboitiz Power Corporation (AboitizPower), the holding company of power-related investments of the Aboitiz Group, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with JERA Co., Inc. (JERA), Japan’s largest power generation company, to jointly assess the potential for greener fuels in power generation. The MOU signing was done in the presence of President Ferdinand “Bongbong” R. Marcos Jr. together with key officials from the Philippine Government. Under the MOU, AboitizPower, and JERA outlined collaborative efforts in assessing the feasibility of ammonia co-fired power generation and further development of the ammonia and hydrogen value chains in the Philippines. This will support the decarbonization efforts of AboitizPower and the Philippines.
Methanol
Costa Group, Proman to drive adoption of methanol as a marine fuel for the cruise industry: Carnival Corporation’s Costa Group and Proman, a top methanol producer, have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to advance the use of methanol as a marine fuel for the cruise industry. The partnership aims to accelerate the energy transition and decarbonization of the existing fleet by improving the supply of sustainable methanol and retrofitting existing vessels, as well as investing in the construction of new methanol-powered vessels. Through this partnership, Costa Group aims to reduce the fleet’s carbon footprint in port and at sea and achieve their goal of greenhouse gas-neutral operation of their fleet by 2050. The Costa Group has already introduced the use of liquefied natural gas (LNG) onboard its ships to reduce emissions, and most ships of the Costa Group are equipped with a shore power connection to operate with almost zero emissions in ports.
Biofuels
PRIO, Norwegian Cruise Line wraps up 1st biofuel tests in Portugal: Portugal’s biofuel producer PRIO has joined forces with Norwegian Cruise Line to complete the first test with advanced biofuels produced and supplied in Portugal. As part of this new partnership with the cruise line Norwegian Cruise Line, PRIO has carried out the first supply in Portugal with ECO Bunkers B30, a fuel with a higher percentage of biofuel incorporation, which thus is expected to achieve a greater reduction in emissions of CO2. This new fuel, ECO Bunkers B30, is a 30% blend of advanced biofuel from waste feedstocks, produced at PRIO’s biodiesel plant and blended at a tank terminal in Aveiro. The flexibility of this blending process makes it possible to scale production according to demand and adjust the percentage of Biodiesel mixtures (up to a 100% renewable product, which allows up to 86% GHG reduction), according to the company.

Cost and availability main barriers to biofuel adoption in maritime: Speaking to Seatrade Maritime News ahead of his presentation at CMA Shipping 2023, Michael D. Kass, PhD, of the Energy Science & Technology Directorate at Oak Ridge National Laboratory said that the US Department of Energy (DoE) has been evaluating biofuels against four main criteria: potential for greenhouse gas reduction, economic feasibility, technical feasibility, and the availability of feedstock resources. While recent biofuel demonstration studies and trials have used biofuels blended with fuel oil in different ratios, Kass said that depending on the biofuel type-any barriers to using 100% biofuel as bunkers are more about cost and availability than technical limitations.
MSC and DB Schenker sign biofuel shipping deal: The two companies have signed an agreement for the use of 12,000 metric tonnes of biofuel components for all of DB Schenker’s consolidated cargo, less-than-container load (LCL), full-container-load (FCL) and refrigerated containers (reefer containers). The 12,000 metric tons of biofuel component will be blended between 20% and 30%, resulting in approximately 50,000 metric tonnes of blended biofuel to be used in MSC’s containerships. The amount of biofuel purchased is enough to save an additional 35,000 metric tons of CO2 equivalents (CO2e) along the entire production chain (well-to-wake) in the market. The equivalent of around 30,000 TEU may be shipped with net-zero CO2 emissions, depending on voyage length.

Ports
AmmPower, and PCCA join hands on green hydrogen solutions: US clean energy company AmmPower has entered into a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Port of Corpus Christi Authority (PCCA) to explore the development of green hydrogen used as feedstock for green fuel and green derivatives production, storage and distribution facility. AmmPower is evaluating the feasibility of working with PCCA to explore the development of a large green hydrogen feedstock for green fuel facility, to produce, store, and distribute these derivatives for use as a carbon-free fuel and a carrier of hydrogen energy. The facility will produce green hydrogen-rich derivatives for domestic and export markets.

Governments
Green maritime tech of the future to become reality: Companies across the UK to benefit from £60 million funding to supercharge the development of clean maritime solutions. The UK’s race to decarbonize the maritime sector has been given another vital boost, with £60 million in government funding distributed to innovative companies nationwide developing futuristic green technology. For the first time, the UK government is funding the development of new clean maritime technology across a 2-year period. Companies in 12 regions around the UK will benefit from the cash, generating highly skilled jobs across the nation and positioning the UK as a world leader in green solutions. The funding comes from the third round of the government’s Clean Maritime Demonstration Competition (CMDC3), which focuses on developing a range of clean maritime technologies including hydrogen, ammonia, electric and wind power.
During the 2-year investment period, successful companies will be required to demonstrate that their projects will work in the real world, helping them to progress towards becoming an everyday reality. Today’s funding comes from the wider £206 million UK Shipping Office for Reducing Emissions (UK SHORE) scheme, announced in March 2022. The CMDC is one of the many initiatives from UK SHORE to fund green technology.
Africa could be green jobs leader: Africa has the potential to become a leading force in seafarer training and could secure many of the new green jobs being created as the global shipping industry moves towards low- and zero-carbon fuels, according to delegates at the Green Shipping Conference held in Accra. The conference is being hosted by the Ghana Maritime Authority in partnership with the Danish Maritime Authority and the UN’s International Maritime Organization (IMO). As explained, a future global center of maritime excellence for seafarer training could be based in Africa, bringing with it more jobs and wider benefits for the region.
Regulations
European Commission sets out rules on renewable hydrogen: The Commission has proposed detailed rules to define what constitutes renewable hydrogen in the EU, with the adoption of two Delegated Acts required under the Renewable Energy Directive. These Acts are part of a broad EU regulatory framework for hydrogen which includes energy infrastructure investments and state aid rules, and legislative targets for renewable hydrogen for the industry and transport sectors. The two Acts are interrelated and both are necessary for the fuels to be counted toward Member States' renewable energy target. They will provide regulatory certainty to investors as the EU aims to reach 10 million tonnes of domestic renewable hydrogen production and 10 million tonnes of imported renewable hydrogen in line with the REPowerEU Plan.

ECSA calls for the inclusion of fuel suppliers under the scope of FuelEU Maritime: The European Community Shipowners’ Associations (ECSA) calls on the European Parliament and the Council to support the mandatory inclusion of fuel suppliers under the scope of FuelEU Maritime as proposed by the European Parliament in Amendment 129. The amendment approved on October 19th says that if a company makes a contract with a fuel supplier for specific fuels, the contract should include provisions that hold the fuel supplier responsible for compensating the company if they don’t deliver the fuels as agreed and the company incurs penalties. The FuelEU Maritime Regulation has been described as crucial for promoting the uptake of sustainable and scalable fuels in shipping. The demand for clean fuels from shipping is growing, but at the same time, the industry is calling on the legislative bodies to ensure that fuel suppliers make clean fuels available in sufficient quantities.
By Maria Bertzeletou
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com













 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 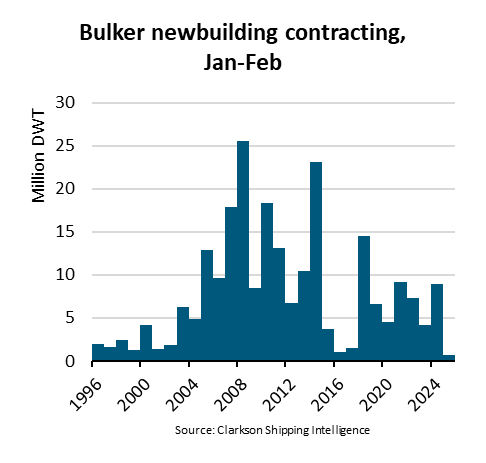 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar