The IMO’s carbon intensity regulations, specifically the carbon intensity indicator (CII) in place since 1 January, are likely to dramatically impact the LNG fleet supply, which could lead to ‘stranded’ assets later this decade. The warning comes from Lloyd’s Register’s gas sector guru, Panos Mitrou. In an opinion piece in the latest issue of the classification society’s Horizons magazine, Mitrou warns that many of today’s LNG carriers are likely to fall into categories ‘D’ or ‘E’ when their CII emission profiles are analyzed. And, as the CII framework tightens over the second half of the decade and methane emissions are included in CII assessments, many vessels could become unemployable, the expert suggests.
Vessels most at risk in the 650-ship deepsea fleet are the 240 LNG carriers powered by steam turbines. Although they do not suffer from methane slip, they are heavy consumers of fuel and do not have boil-off management systems. Their day rates are substantially lower than LNG tankers equipped with four-stroke dual-fuel diesel-electric (DFDE) engines (about 190 ships) and the 215-odd latest generation low- and high-pressure two-stroke vessels.
In parallel, LNG was the fuel of choice amongst owners ordering ships for operation on alternative fuels in 2022. According to analysis by DNV, more than 80% of such vessels – 222 ships – were contracted last year compared with 35 ships that will operate on methanol, the second most popular alternative fuel. The figures do not include contracts for 50 LPG tankers capable of dual-fuel LPG operation Thirty of the methanol-fuelled vessels contracted last year are large containerships. The orders bring the methanol-fuelled total to 82 ships.
About three-quarters of the LNG-fuelled vessels were container ships and pure car and truck carriers ordered last year. Product carriers came next, with 9% of orders. The tally of LNG-fuelled ships either in operation or on order now totals 876 ships, according to DNV’s figures, with 104 vessels powered by LNG commissioned during 2022.
Research Studies
DNV, RSI kick start Baltic and North Sea green fleet renewal study: DNV and the Responsible Shipping Initiative (RSI), an alliance of Swedish dry bulk charterers, have launched a feasibility study to develop a commercial framework for orders of green-fuelled newbuilds to decarbonize the sea transport supply chain in the Baltic and North Sea areas and beyond. With this project, the RSI members aim to reduce their Scope 3 emissions and meet their sustainability targets in response to growing market demands and regulatory reporting requirements on environmental performance across the value chain.
The RSI members see a strong need for green new builds to replace the aging shortsea fleet operating in the Baltic and North Sea dry bulk trade. Many of the vessels are expected to reach the end of their economic life in the next five to 10 years.
Alliances for Decarbonization
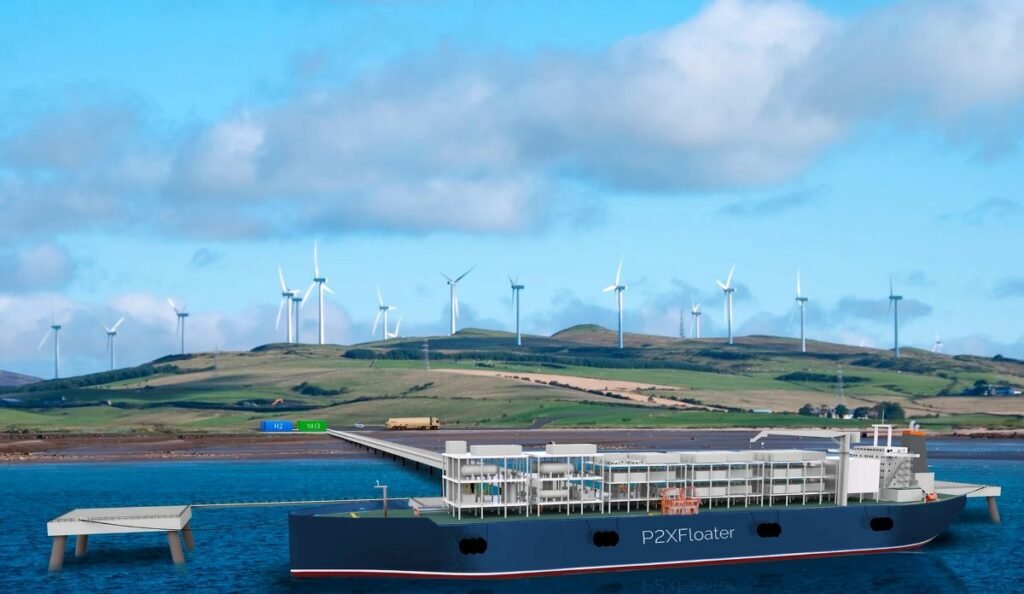
H2Carrier to develop windfarm in Greenland to produce green ammonia: Norway’s H2Carrier and the Greenland-based company Anori have signed a Letter of Intent with the purpose of developing the first commercial offshore wind farm in Greenland as part of a project to produce and export green ammonia.
The wind farm is projected to have a capacity of 1.5 GW and supply power to H2Carrier’s floating production vessel for hydrogen and green ammonia, the so-called P2XFloater™. Green ammonia will be stored in tanks onboard the vessel, then exported to smaller shipping vessels and carried to the international market for ammonia, the companies said.

Jotun partners in Norwegian zero-emissions project: Sea Zero is a project Hurtigruten Norway started in the spring of 2022 and its ambition is to enable zero-emission passenger and freight transport along the Norwegian coast by 2030. Together with 13 partners, Hurtigruten has been granted NOK 67m from Grønn Plattform, a scheme that contributes to research and innovation-driven green transformation and lower greenhouse gas emissions, and is managed by the Research Council, Innovation Norway, and Siva. With the funding, all the partners have planned to start the research and development part of the project early in 2023.

Industry Actions
BP buys a US biogas company in a push to reduce carbon intensity: UK-headquartered energy giant BP has completed the acquisition of Archaea Energy, a Texas-based renewable natural gas (RNG) company. Archaea Energy operates 50 RNG and landfill gas-to-energy facilities across the U.S., producing around 6,000 barrels of oil equivalent a day (boe/d) of RNG. Its production would be expected to provide an immediate 50% increase to BP’s biogas supply volumes.

Chinese shipowners look to decarbonize through ICS: The International Chamber of Shipping (ICS) has welcomed the China Shipowners’ Association (CSA) as a Full Member of ICS. The CSA will join the ICS Board, which oversees the policy positions ICS presents on behalf of shipowners worldwide with the industry’s global regulators, including IMO and ILO. Given the importance of China as a major shipping nation, the membership of CSA confirms the legitimacy of ICS, through its structure comprising member national (and regional) shipowner associations to speak on behalf of the global industry.
Next Generation of Vessels
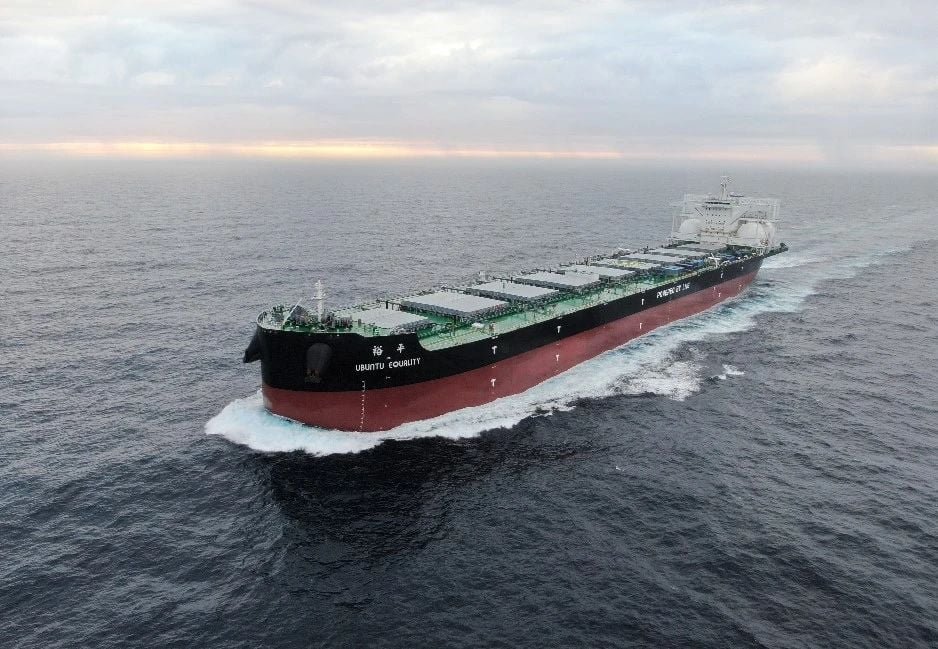
2nd LNG-fuelled bulker joins U-Ming’s fleet: Chinese shipbuilder Shanghai Waigaoqiao Shipbuilding has started off the year with the delivery of a 190,000-ton dual-fuel LNG bulk carrier named Ubuntu Equality. The giant vessel was built for Taiwanese bulk carrier company U-Ming Marine and it is a sister ship to Ubuntu Harmony, delivered at the end of December.

MOL to build a sail-fitted hydrogen-producing ship: Mitsui OSK Lines (MOL) plans to launch the construction of Wind Hunter, a hydrogen-producing vessel outfitted with multiple rigid sails, in 2024. The construction forms part of the company’s Wind Hunter program, which seeks new applications for hydrogen fuel and wind power. The project intends to use MOL’s rigid, collapsible sail technology developed under the Wind Challenger project on vessels capable of capturing that power during high wind periods to generate hydrogen for use during lower wind sections of the voyage. Namely, the zero-emission seagoing cargo ship, with a total length of 60 to 70 metres, would not need to refuel as it would use wind assisted-propulsion when there are strong winds in combination with hydrogen produced onboard to sail.

LNG/Hydrogen-fuelled VLCC design from SWS gets AiP: RINA has announced the Approval in Principle (AiP) for the first very large crude carrier (VLCC) from Shanghai Waigaoqiao Shipbuilding (SWS) for using an innovative propulsion arrangement that reduces of ship’s resistance by 5-10%. The LNG/Hydrogen-fuelled vessel general arrangement developed by SWS is based on the result of a joint project with Marin, the Liberia Administration, Wartsila, ABB, Helbio and RINA, which will meet the IMO targets for 2050 through the use of the ship’s fuel LNG combined with hydrogen produced onboard.
Celsius linked to order of up to 8 LNG carriers at CMI: China Merchants Industry Holding (CMI), a manufacturing flagship of China Merchants Group, has won a contract for the construction of up to eight 180,000 cbm LNG carriers from an undisclosed European shipowner. The company behind the contract, which includes four firm orders plus four options, is believed to be Danish shipowner Celsius Tankers. The order is being reported just a month after Celsius placed an order for an additional 180,000 cbm LNG carrier at Samsung Heavy Industries pushing its LNG carrier fleet to 14 vessels. The company has a fleet of over 45 ships, which include chemical and product tankers, and container feeders.
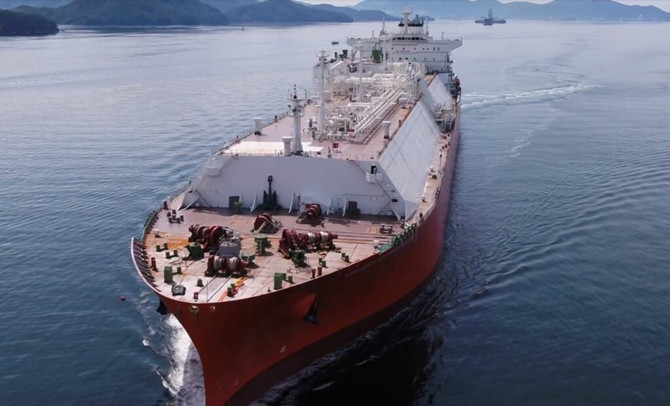

NYK Line and partners obtain ClassNK’s AiP for ammonia FSRB: Japanese shipping major NYK Line and its partners Nihon Shipyard (NSY) and IHI Corporation (IHI) have received Approval in Principle (AiP) from the classification society ClassNK for an ammonia floating storage and regasification barge (A-FSRB). According to ClassNK, this is the world’s first AiP for A-FSRBs handling ammonia as cargo. The A-FSRB is an offshore floating facility that can receive and store ammonia that has been transported via ship as a liquid as well as warm and regasify ammonia according to demand and then send it to a pipeline onshore.

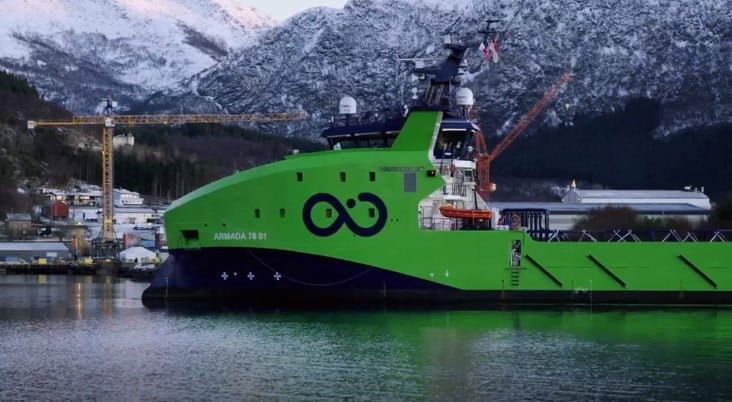
The first high-tech ammonia-ready Armada vessel arrives in Europe: The first of eight robotic vessels that will form part of Ocean Infinity’s high-tech Armada fleet has arrived in Norway for equipment installation. The vessel, built by Vard Vung Tau in Vietnam, arrived at Vard Søviknes for remote system outfitting and payload equipment installation.
According to Ocean Infinity, this first ship is expected to enter service on offshore data acquisition tasks in the coming months. The first two robotic vessels left Vietnam in November for their maiden voyage, after they were delivered to the marine robotics company.

Ferries
Construction of Scandlines’ zero-emission ferry making headway at Cemre: Scandlines’ new zero-emission ferry is starting to take shape at the Cemre shipyard in Turkey. Danish ferry operator said in an update that two-thirds of the steel plates have now been cut at the shipyard, adding that the ferry currently consists of eight sections which have already been placed on the bedding. Another 16 sections are under construction. The keel for the vessel was laid back in September. It was said at the time that the ship will not be built around a single keel but rather with several hull sections.

Technology
HHI methanol engine completes acceptance test: Hyundai Heavy Industries Engine & Machinery Division (HHI-EMD) has successfully completed the FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) of its H32DF-LM methanol dual fuel HiMSEN engine, undertaken in collaboration with shipowner Maersk, at the HiMSEN production factory in Ulsan, South Korea. The H32DF-LM engine demonstrated excellent performance and quality during the tests. It is a 5,400bhp gen-set engine that selectively uses methanol and diesel fuel and is characterized by significantly reduced GHG and emissions of sulphur and nitrogen oxides. In addition, it employs special materials to prevent corrosion. The engine applies the Diesel cycle with electronically controlled fuel injection methods in methanol mode to enable high-power operation in stable conditions.
MacGregor to supply RoRo equipment for K Line’s LNG-powered newbuilds: MacGregor, part of Cargotec, has secured a large order to supply RoRo equipment for two 6,900 CEU Pure Car and Truck Carriers (PCTCs) to be built at Shin Kurushima Toyohashi Shipbuilding for K Line in Japan. The order was booked into Cargotec’s 2022 third-quarter order intake. The first vessel is scheduled to be delivered to the owner in the first quarter of 2025 and the second in the second quarter of 2025. MacGregor’s scope of supply consists of design, supply, and installation assistance for a stern ramp, a side ramp, three sets of movable ramps, a ramp cover, and a mobile deck lifter for each vessel.

Novel monitoring technology undergoing tests at Danish CO2 storage project: A new monitoring technology that is said to ensure more frequent checks of the future CO2 storage and results in less impact on the environment is currently being tested for Project Greensand in the North Sea. Magseis Fairfield reported last week that it had mobilized its MASS III nodes and modular source for testing the new CO2 monitoring technique developed by SpotLight. Monitoring is said to take place by placing seabed nodes at 16 carefully selected points on the seabed. The collected data is compared with previous images of what the sandstone reservoir looks like and therefore Project Greensand can uncover where the CO2 is located. The work is part of the project’s pilot phase and is being carried out by Esvagt Innovator.
Shipyards
Steel cut for Maersk’s 16,200 TEU methanol-fuelled boxship: Container shipping major Maersk has launched the construction of its 16,200 TEU dual-fuel containerships that can run on green methanol. Namely, South Korean shipbuilder Hyundai Heavy Industries hosted a steel-cutting ceremony for what is believed to be the first vessel from the series on November 28, 2022, based on a social media update from Maersk. Maersk has a total of 19 methanol-powered container carriers on order at Hyundai Heavy Industries and Hyundai Mipo Dockyard. These include six vessels with a nominal capacity of 17,000 TEU ordered last October, twelve 16,000 TEU boxships, and one feeder ordered in 2021. The dual-fuel vessels will be capable of burning methanol as well as conventional low-sulfur fuel.

Fuels
Pilbara Clean Fuels, Oceania Marine join hands on eLNG project: Pilbara Clean Fuels (PCF) has teamed up with Oceania Marine Energy on the provision of low-carbon footprint LNG production and marine bunkering capability at Port Hedland, Western Australia. PCF is pursuing the development of an electrified liquefied natural gas (eLNG) plant in Port Hedland, world’s largest iron ore export port, principally to produce marine bunker fuel. The project aims to provide an Australian LNG fuel supply capability through a new facility for the conversion of pipeline natural gas to LNG, responding to market demand for cleaner marine bunker fuel for iron ore carriers operating ‘round-trip’ voyages out of Port Hedland.

Chevron, ONE wrap-up biofuel bunkering on 4,800 TEU containership: Oil major Chevron has teamed up with Singapore-based shipping giant Ocean Network Express (ONE) to complete inaugural biofuel bunkering on a 4,800 TEU containership. As informed, the bunkering operation was witnessed by the Singapore Trade Data Exchange (SGTraDex), a digital infrastructure that facilitates the sharing of data between supply chain ecosystem partners. The transaction saw the transfer of 992.2MT VLSFO-B24, biofuel in 6, 7 P, and S deep tanks from bunkering tanker Marine Rose to containership
MOL Endowment.
Ports
RWE and Sempra firm up 2.25 mtpa Port Arthur LNG deal: US LNG company Sempra Infrastructure has finalized a long-term sale and purchase agreement with RWE Supply & Trading, a subsidiary of RWE, for the supply of liquefied natural gas (LNG) from its Port Arthur LNG Phase 1 project under development in Jefferson County, Texas. Under the agreement, approximately 2.25 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) will be delivered on a free-on-board basis for 15 years. The agreement is said to also provide a framework to explore ways to lower the carbon intensity of LNG produced from the Port Arthur LNG Phase 1 project through GHG emission reduction, mitigation strategies, and a continuous improvement approach.
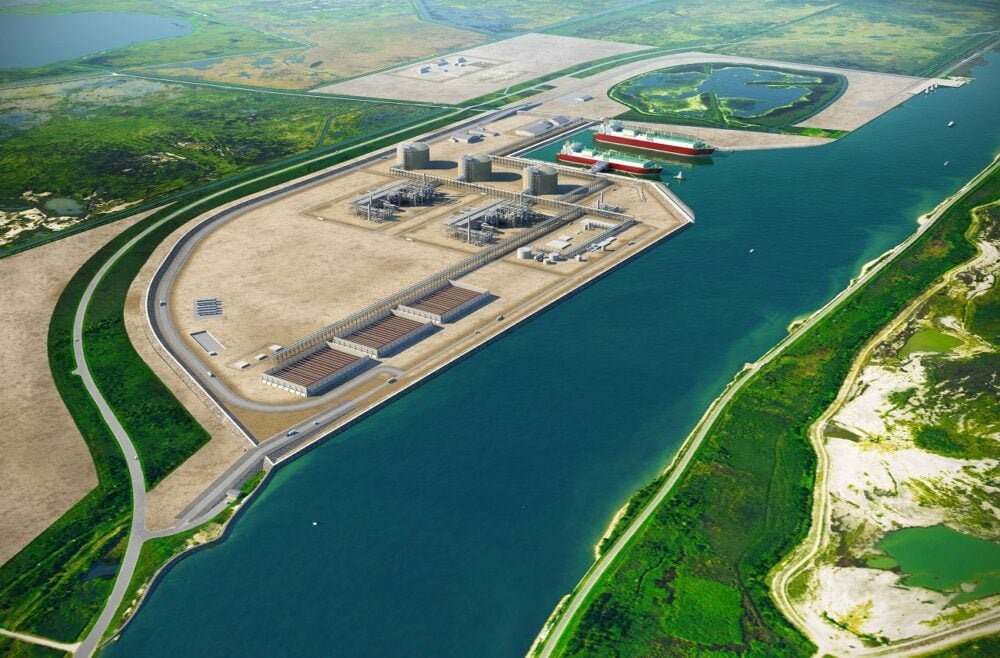

US LNG company Sempra Infrastructure has finalized a long-term sale and purchase agreement with RWE: Supply & Trading, a subsidiary of RWE, for the supply of liquefied natural gas (LNG) from its Port Arthur LNG Phase 1 project under development in Jefferson County, Texas. Under the agreement, approximately 2.25 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) will be delivered on a free-on-board basis for 15 years. The agreement is said to also provide a framework to explore ways to lower the carbon intensity of LNG produced from the Port Arthur LNG Phase 1 project through GHG emission reduction, mitigation strategies, and a continuous improvement approach.
Ship Financing
TT-Line gets a financial boost for its dual-fuel RoPax ferry: German bank KfW IPEX-Bank has revealed it will provide financing in the amount of €30 million for compatriot shipping company TT-Line’s dual-fuel roll-on/roll-off passenger (RoPax) ferry. Dual-fuel RoPax ferry Nils Holgersson is one of two new green ships delivered to TT-Line in 2022. With a length of 230 meters and a width of 31 meters, each RoPax has a capacity of 800 passengers and over 200 trucks and trailers. In addition to the environmentally friendly dual-fuel engines, which TT-Line has already used with Bio-LNG, they are equipped with further modern technologies and innovative solutions, including heat-insulating windows and 32 charging stations for electric cars.
Regulations
Israel introduces 0.1% sulphur directive: Israel is jumping ahead of littoral states in the Mediterranean, introducing a sulphur emission control area (ECA) in its waters from the start of next month. Effective February 1, ships calling at Israeli ports must burn marine fuels with a 0.1% maximum sulphur content. Last month, member states of the International Maritime Organization agreed to create an ECA across the Mediterranean in 2025. Other ECAs around the world include the Baltic Sea, the North Sea, the North American area covering designated coastal areas of the United States and Canada, and the United States Caribbean Sea area around Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands.

By Maria Bertzeletou, Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com















 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 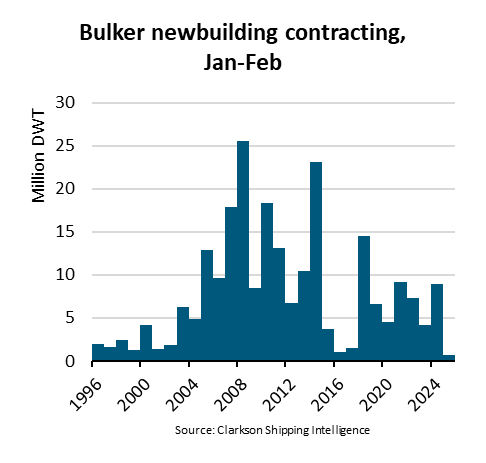 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar