To achieve 2030 national climate goals, 700 low-emission and 400 zero-emission ships will be required in Norway alone, according to Norwegian maritime organizations and the shipping industry.
The Norwegian collaboration was formally announced today (7 November) at a high-level launch event during COP27 in Egypt. Collaboration participants comprise GCE Blue Maritime (maritime cluster center of excellence), NCE Maritime CleanTech (Cluster for Clean Maritime Solutions, Næringslivets Hovedorganisasjon (The Confederation of Norwegian Enterprise, NHO), Norsk Industri (The Federation of Norwegian Industries), Norges Rederiforbund (Norwegian Shipowners Association), Kystrederiene (Norwegian Coastal Shipowners), Maritime Forum (Maritime Forum industry association), Havila Kystruten (Havila Voyages), Hurtigruten, Kongsberg (marine technology) and DNV (classification society). The partners have pledged to achieve the emission reduction targets in response to the Green Shipping Challenge formulated jointly by the Governments of Norway and the United States.
The Green Shipping Challenge, whose main goal is to accelerate the global transition to green shipping, was launched in May 2022 as part of a joint statement on climate by Norwegian Prime Minister Johas Gahr Støre and U.S. President's Special Envoy for Climate Affairs John Kerry.
Participants in the Norwegian collaboration have committed to reducing emissions from shipping by 50% by 2030, which is in line with Norway’s national climate targets. This complements the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) current target to reduce CO2 emissions from global shipping by at least 40% by 2030 and 70% by 2050.
Norwegian financial partners with maritime patronage commit to using capital instruments to support environmentally friendly measures and projects by providing venture capital and financial advisory services. In addition, the Norwegian government will support green initiatives and the development of fossil-free energy infrastructure. In addition to efforts to improve the energy efficiency of existing vessels, the partners will also take steps to develop, design, and, build zero-emission vessels of the future.
Tools for Emissions
UN launches satellite system to track methane emissions: The United Nations has announced a new satellite-based system to detect emissions of methane and allow governments and businesses to respond. The Methane Alert and Response System (MARS) is a data-to-action platform set up as part of the UNEP International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO) strategy to get policy-relevant data into the right hands for emissions mitigation. Developed in the framework of the Global Methane Pledge Energy Pathway – with initial funding from the European Commission, the US Government, Global Methane Hub, and the Bezos Earth Fund – MARS will allow UNEP to corroborate emissions reported by companies and characterize changes over time. MARS will be implemented with partners including the International Energy Agency, and the UNEP-hosted Climate and Clean Air Coalition.
Alliances for Decarbonization
Chinese majors set up a new sustainable shipping initiative: China Classification Society (CCS) has joined forces with several major Chinese marine industry companies to launch the Sustainable Shipping Innovation and Development Initiative (SSIDI). The partners will now work closely together to explore and research alternative fuels. Furthermore, the initiative will include research work focused on the economy, safety, technology maturity, policies and regulations, fuel availability, market mechanism, and other aspects of alternative fuels for shipping.
Chevron and MOL to study CO2 shipping from Singapore to Australia: Chevron Corporation and Mitsui OSK Lines (MOL) have signed a joint study agreement on the feasibility of transporting liquified carbon dioxide (CO2) from Singapore to permanent storage locations offshore Australia. Chevron and MOL will explore the technical and commercial feasibility of initially transporting up to 2.5m tonnes per annum of liquified CO2 by 2030. The study will complement work to be advanced by a recently announced consortium to explore solutions for large-scale carbon capture, transport, and permanent storage of CO2 from Singapore. Through its part in three joint ventures, Chevron was also recently granted an interest in three greenhouse gas assessment permits offshore Australia. Earlier this year MOL received approval in principle from ClassNK for its large CO2 carrier design, capable of transporting 1m tons of CO2 every year.
MPC Container Ships opts for zero44’s CO2 management tech: Norwegian company MPC Container Ships has partnered with Berlin-based zero44 to use its digital CO2 management solution for its entire fleet. The solution was selected after a joint development and testing phase that began in February 2022. The software focuses on the implications of the CII and the EU ETS regulation introduced by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) and the European Union (EU). With zero44’s digital solution, shipping companies gain control over the emissions of their vessels as well as concrete decision-making aids for their commercial planning.
 Samsung and KSS Line to develop hydrogen and ammonia seaborne trades together:
Samsung and KSS Line to develop hydrogen and ammonia seaborne trades together: Samsung C&T Corp, the construction and trading arm of South Korea’s Samsung Group, is teaming with compatriot shipping firm KSS Line is developing a fleet of hydrogen and ammonia carriers. KSS Line is the country’s only owner with current experience of shipping ammonia. The two parties will work to source hydrogen and ammonia overseas and bring it back to South Korea where Seoul has indicated the two energy forms will be an important part of the nation’s energy mix in the coming decades. South Korean shipyards are busy bringing a host of hydrogen and ammonia carrier designs to market.

Industry Actions
KBR secures work on Australia’s first industrial-scale green hydrogen project: US engineering company KBR and Belgium engineering firm Tractebel, part of ENGIE, have been appointed as the Owners Engineer for the Yuri project, a new renewable hydrogen facility in the Pilbara, Western Australia. The Yuri project is being co-developed by utility company ENGIE and ammonia producer Yara Pilbara Fertilisers. Together, the companies aim to deliver a green hydrogen plant that integrates with Yara’s existing ammonia plant on the Burrup Peninsula in Western Australia’s Pilbara region.
 Google calls for more restrictive ‘green’ hydrogen rules:
Google calls for more restrictive ‘green’ hydrogen rules: US technology giant Google, leading a group of several companies including Spanish utility Iberdrola and the Dutch natural gas firm Eneco, has urged the European Commission (EC) to adopt strict rules on what can be classified as ‘green’ hydrogen. On 2 November, Google, Iberdrola, and Eneco, among others, addressed an open letter to the EC ‘as companies committed to advancing the goals to make Europe the first climate-neutral continent by 2050’. The role of hydrogen produced by renewable electricity as a key tool to accelerate decarbonization across the economy and reduce dependency on fossil fuels was highlighted in the letter.
 DP World earmarks $500 million to cut CO2 emissions across its business:
DP World earmarks $500 million to cut CO2 emissions across its business: Dubai-based logistics heavyweight DP World plans to invest up to $500 million to cut CO2 emissions from its operations by nearly 700,000 tonnes over the next five years. The move was announced by the company’s Chairman and Group CEO, Sultan Ahmed Bin Sulayem while he was addressing delegates at the UN Climate Conference (COP 27) in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt. DP World’s plans include replacing its global fleet of assets from diesel to electric, investing in renewable power and exploring alternative fuels for vessels and port vehicles. As a partner, DP World has committed to long-term strategic collaboration and contribution to the development of zero-carbon technologies and solutions for the maritime industry. DP World noted that it was also working with local communities where it operates to establish carbon offset schemes and carbon sinks such as mangrove forests.

Classification
LR launches ‘Zero Ready Framework’ for vessels operating on zero carbon fuels: Lloyd’s Register (LR) has launched a five-level framework for assessing the actual readiness of a vessel for the transition to zero carbon fuels. Published by LR’s Maritime Decarbonisation Hub, ‘Zero Ready Framework – helping to ensure shipping can deliver our zero-emissions future’, ranks vessel readiness for zero carbon fuel operations from 1 (highest level of readiness) to 5 (lowest level of readiness), and measured on a well-to-wake basis.
The framework has been created to offer clarity around the term ‘readiness’ which is used in multiple ways across the shipping industry. The rankings were developed based on observations that some shipowners have had a design for conversion to zero carbon fuel done as a paper exercise, without a plan for how the conversion would be carried out. Others have some or all the required equipment (for example engine, tank, pipework, fuel management system) already installed. Another group of vessels has a dual-fuel engine that could run on zero-carbon fuel but may require an engine retrofit to do so.

Next Generation of Vessels
BULKER
Himalaya’s LNG-powered bulkers hit the water at New Times Shipyard: New Times Shipbuilding in China has launched two LNG dual-fuel bulk carriers being built for Bermuda-based bulk carrier company Himalaya Shipping. The two 210,000 dwt vessels, named Mount Norefjell and Mount Ita, are the first two vessels from a series of twelve newcastlemax dry bulk vessels under construction at the yard. The ships will also be fitted with scrubbers allowing them to run on high-sulfur fuel oil as well as LNG and low-sulfur fuel oil. The shipowner expects that the scrubber installation would increase the flexibility of the vessels and that the investment would be paid back in less than 1.5 years. According to Himalaya Shipping, the design of the vessels will also allow for future conversion to next-generation fuels.
 More Norwegian hydrogen-powered bulkers to enter service:
More Norwegian hydrogen-powered bulkers to enter service: Norway’s Halten Bulk has moved to build a pair of hydrogen-fuelled bulkers following NOK142m ($13.8m) funding from government enterprise Enova. Halten Bulk, owned by Brødrene Nordbø, Egil Ulvan, and Strand Shipping, was founded in 2014 and currently operates seven short-sea bulk vessels. The two new vessels have been designed by Norwegian Ship Design, which now has orders for five hydrogen-fuelled vessels. They belong to the so-called “Powered by Nature” concept developed in cooperation with Egil Ulvan, which earlier this year unveiled plans for a zero-emission hydrogen-fuelled self-discharging bulker set to enter service in 2024.

Skarv Shipping to build four multi-fuel shortsea bulkers: Grieg Edge, the innovation hub of Norwegian shipping group Grieg Star, has teamed up with compatriot Peak Group AS to establish a joint venture named Skarv Shipping Solutions. The JV founders said that the company aims to help ship and cargo owners reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases and reach their climate goals. Earlier this year, Grieg Edge won approval in principle from DNV for its green ammonia tanker MS Green Ammonia which also runs on green ammonia developed jointly with LMG Marin and Wärtsilä. The tanker is a part of the larger Berlevåg project in the north of Norway where a group of Norwegian companies intends to use wind from Raggovidda to produce green ammonia.

CONTAINER
Wan Hai’s new eco-friendly boxship trio named in Japan: Taiwanese shipping company Wan Hai Lines has held a naming ceremony for three new eco-friendly 3,013 TEU containerships. The naming ceremony took place at Japan Marine United Corporation Kure Shipyard on 7 November. The vessels were named WAN HAI 355, WAN HAI 357, and WAN HAI 360. The design of the 3,013 TEU series takes energy efficiency and environmentally-friendly aspects into account. The fourth vessel WAN HAI 355 will be delivered on 8 November and deployed in Asia-America Service.

METHANOL BUNKERING
Stena and OljOla to build methanol bunkering vessel for North Europe: Swedish companies Stena Oil, Stena Teknik, and OljOla have entered into a joint venture agreement to build a bunker supply vessel designed to carry chemicals as per IMO Type II, including methanol and various bio-fuels. The new building 2000 dwt oil- and chemical tanker is designed by Kuzey and is being built by GENKA Shipbuilding in Tuzla, Turkey. The project is a joint venture involving OljOla Shipping as owner with full technical management, Stena Oil as commercial operator, and Stena Teknik as project and new building management.

CRUISE
P&O Cruises’ LNG-fuelled cruise ship Arvia set for delivery: P&O Cruises’ second LNG-powered Excel-class cruise ship Arvia is set for delivery, German shipbuilding company Meyer Werft revealed. The new cruise ship is equipped with the cleanest propulsion system currently available to the shipping industry, an LNG propulsion system, according to Meyer Werft. This means that Arvia is built to be future-proof and, in perspective, can even be operated in a climate-neutral manner using green regenerative LNG. LNG propulsion is seen as a solution that eliminates nitrogen oxides and particulate matter in addition to reducing CO2 emissions, while sulfur oxides are eliminated.
 BIO-SEA’s BWTS for the world’s largest LNG-powered cruise ship:
BIO-SEA’s BWTS for the world’s largest LNG-powered cruise ship: MSC World Europa, the first in a series of four next-generation cruise ships to join the MSC Cruises fleet, has been delivered with a ballast water treatment system (BWTS) from BIO-SEA by BIO-UV Group. French shipbuilding company Chantiers de l’Atlantique delivered the vessel in Saint-Nazaire on 24 October. The ship measures 580.3 meters in length and can accommodate 6,762 passengers with a crew of 2,138.

OFFSHORE
ABS green-lights COSCO’s ammonia-fueled vessel design: COSCO Shipping Heavy Industry Co. and COSCO Shipping Heavy Industry Technology have won two approvals in principle from the ABS classification society for their ammonia-fueled vessel and ammonia supply system designs which are being trialled on a tugboat.
Given the challenging characteristics of ammonia, ABS conducted a comprehensive review and risk assessment focused on ammonia filling, storage, supply, ventilation, and emergency handling in the AIP process to address the safety and reliability of the systems.
Fuels
Green methanol supply slated for Jebel Ali: Another green methanol fuel site is set to open at a key maritime gateway. Averda, a waste management, treatment, and recycling company, and WasteFuel, a developer of bio-refineries, announced during the COP27 climate conference, their partnership to develop the first commercial-scale municipal waste to renewable methanol plant in the Middle East. The location for the first plant is likely to be Jebel Ali, the premier port in the United Arab Emirates. The plant will produce renewable methanol for shipping from unrecyclable waste currently being collected and disposed of by Averda.
Yara and MOL team up to strengthen the ammonia supply chain: Yara Clean Ammonia, a subsidiary of Norwegian fertilizer company Yara International ASA, and Japanese shipping giant Mitsui O.S.K. Lines (MOL) have agreed to work together to strengthen the ammonia supply chain. According to MOL, the collaboration includes but is not limited to using ammonia as a marine fuel. With this collaboration, the companies aim to jointly lead the industries to accelerate decarbonization. In addition to partnering with MOL, Yara has signed a collaboration agreement with Brooklyn-based technology startup Amogy.

Biofuels
Scandinavian Biogas secures multi-year Bio-LNG supply deal worth $27 million: Swedish biogas producer Scandinavian Biogas has signed a multi-year agreement for the supply of liquid biogas (Bio-LNG) to the transport sector in the Nordic region. As disclosed, the deliveries of liquefied biogas under the agreement will begin shipping in 2023 and are intended from Scandinavian Biogas’ production facilities in Sweden. According to the company, the large volumes of Bio-LNG will contribute to a sustainable circularity for the transport sector. The order is worth approximately SEK 300 million, which is said to be in line with Scandinavian Biogas’ communicated growth plans. Liquid biogas comes from organic waste that is converted into biofertilizer and biogas, upgraded, and liquefied.
XFuel developing affordable marine biofuels at scale: XFuel is developing modular, scaleable, refineries for a second-generation biofuel that is compatible with existing ISO marine fossil fuel specifications and the company says is considerably lower cost than existing biofuels. XFuel uses a patented process to convert biomass waste into drop-in biofuels and currently has a demonstration plant in Spain with an annual capacity of around 1m liters and is now gearing up for larger projects around the world that would be capable of supplying the volumes required by the marine industry.
Green Corridors
Major Californian ports partner with MPA Singapore on the green, digital shipping corridor: The Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA), Port of Long Beach (POLB), Port of Los Angeles (POLA), and C40 Cities have begun discussions to establish a green and digital shipping corridor between Singapore and the San Pedro Bay port complex. According to the announcement, the corridor is expected to focus on low- and zero-carbon ship fuels and digital tools to support the deployment of low- and zero-carbon vessels. This collaborative effort supports the Green Shipping Challenge launched during the World Leaders’ Summit at the 27th United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP27) in Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt.
 NWSA, Busan Port Authority collaborate on decarbonization initiative:
NWSA, Busan Port Authority collaborate on decarbonization initiative: Northwest Seaport Alliance announced its newest decarbonization effort and partnership with Busan Port Authority, as part of the Green Shipping Challenge at the 27th Conference of the Parties (COP 27). The Northwest Seaport Alliance (NWSA), a marine cargo operating partnership of the US port of Seattle and Tacoma, announced a partnership with the Republic of Korea, the Busan Port Authority, and the United States government to study the feasibility of creating a green cargo corridor between NWSA and the Busan Port Authority's cargo gates. Green Shipping Challenge is a new initiative of the United States and Norway, which according to the Northwest Seaport Alliance aims to highlight global actions and concrete measures taken to decarbonize the international shipping industry.

Ports
Spain’s Gandia to house Europe’s 1st energy self-sufficient port: The Port of Gandia is set to become Europe’s first energy self-sufficient port after the installation of the solar energy plant, the Port Authority of Valencia (PAV) has revealed. Valenciaport has awarded a contract for the installation and maintenance of the solar energy plant to compatriot firm Electromur. The project, which has a capacity of 990 MWh/year, is expected to make Gandia the first European port to be energy self-sufficient. Valenciaport plans to inject €130 million in sustainability actions to meet the strategic objective of 2030 zero emissions, which will reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote energy security.
Port of Aberdeen gets £200,000 to speed up its drive to net zero: The UK’s Port of Aberdeen has been awarded more than £200,000 from the UK Government to accelerate its drive to Net Zero by 2040.
The ‘Port Zero’ feasibility study, which is part of the Clean Maritime Demonstration Competition Round 2 (CMDC2), will analyse future port power demands, assess low carbon energy sources for equipment (e.g., cranes, tugs, pilot boats) and quayside infrastructure, and help develop a roadmap to decarbonize port operations. The shipping study will develop a detailed project plan for the world’s first hydrogen-powered zero-emission crossing demonstration from Port of Aberdeen to Norway in 2024, which is an economically important potential green shipping corridor route.

Governments
France vows to boost spending on developing zero-emission ships: France’s secretary of state in charge of maritime affairs, Hervé Berville, has set aside €300m ($302m) under the government’s France-Mer 2030 plan to get the country closer to building zero-emissions vessels. While only 12% of the ships used in France are built in the country, compared to 80% in 1980, Berville stressed the need to make future zero-carbon ships “as French as possible, from its keel to its fuel cell”. At the same conference, the chairman of CMA CGM, Rodolphe Saadé, announced he would give the new France-Mer 2030 fund €200m in additional funding. Other European nations, notably the UK and Norway, have been talking up prospects of boosting their shipbuilding roots with the coming greening of the industry.
Regulations
EC launches €3 bln call for clean tech projects to deliver on REPowerEU and end dependence on Russian fossil fuels: The call was opened under the EU Innovation Fund, a funding program for the demonstration and commercialization of innovative low-carbon technologies. With this call, EC focuses on the priorities of the REPowerEU plan and aims to provide additional support toward ending the EU’s dependence on Russian fossil fuels.

By Maria Bertzeletou, Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com



















 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 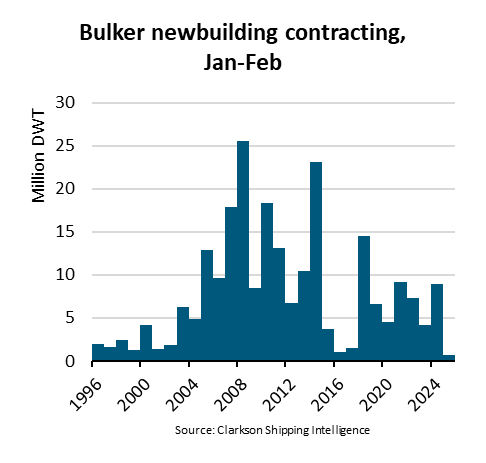 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar