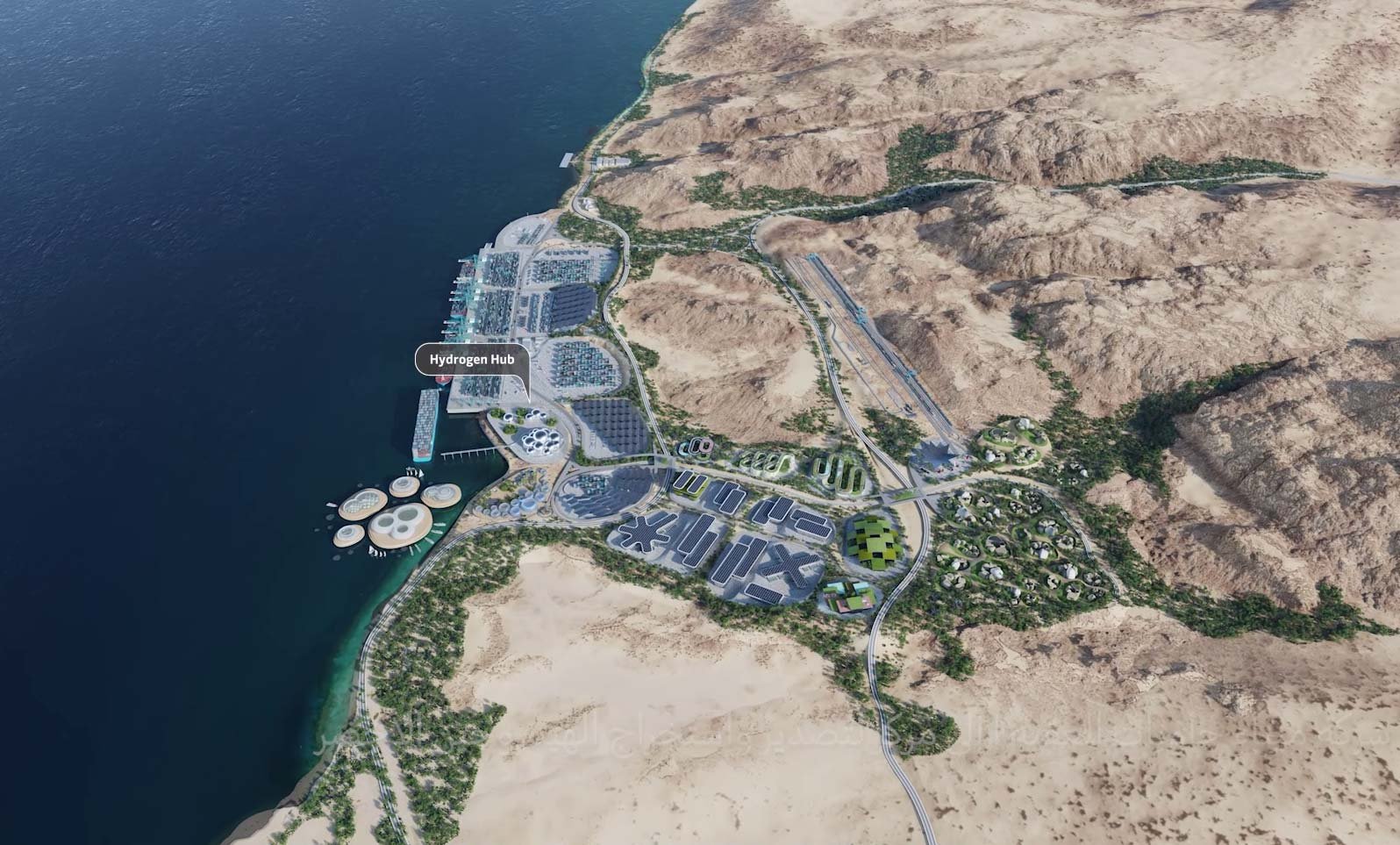
U.S. engineering firm KBR has been awarded a technology contract for a low-carbon blue ammonia project in the United States, which is being developed by Dutch hydrogen products manufacturer and distributor OCI NV. KBR has been selected by EPC contractor Tecnimont S.p.A. to provide the technology license, basic engineering, proprietary equipment, and catalyst for the 1.1 million ton per year blue ammonia plant. The project, which is scheduled for completion by 2025, is designed to transition from blue to green ammonia production once green hydrogen becomes more widely available.
The Finnish technology group Wärtsilä has partnered up Capital Gas Ship Management Corp. to develop a new Fleet Decarbonization Program aimed at boosting the efficiency of the company’s LNG carrier fleet. The agreement was signed in June 2022 and will be applied to a fleet of six 174,000 cbm LNG carriers within the Capital Gas management portfolio. To comply with the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) upcoming Energy Efficiency for Existing Ships Index (EEXI) and CII protocols, fleet operators are faced with the complex task of selecting the optimal solution. Therefore, the program will provide a detailed Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) compliancy analysis of the vessels, predicting the fleet’s status in reference to the 2030 targets.
The plan was revealed as the company joins the First Movers Coalition (FMC), which targets hard-to-abate sectors including aluminium, aviation, chemicals, concrete, shipping, steel, and trucking, which are responsible for 30% of global emissions. The company also sees bright growth prospects for the utilization of biofuels on its ships.
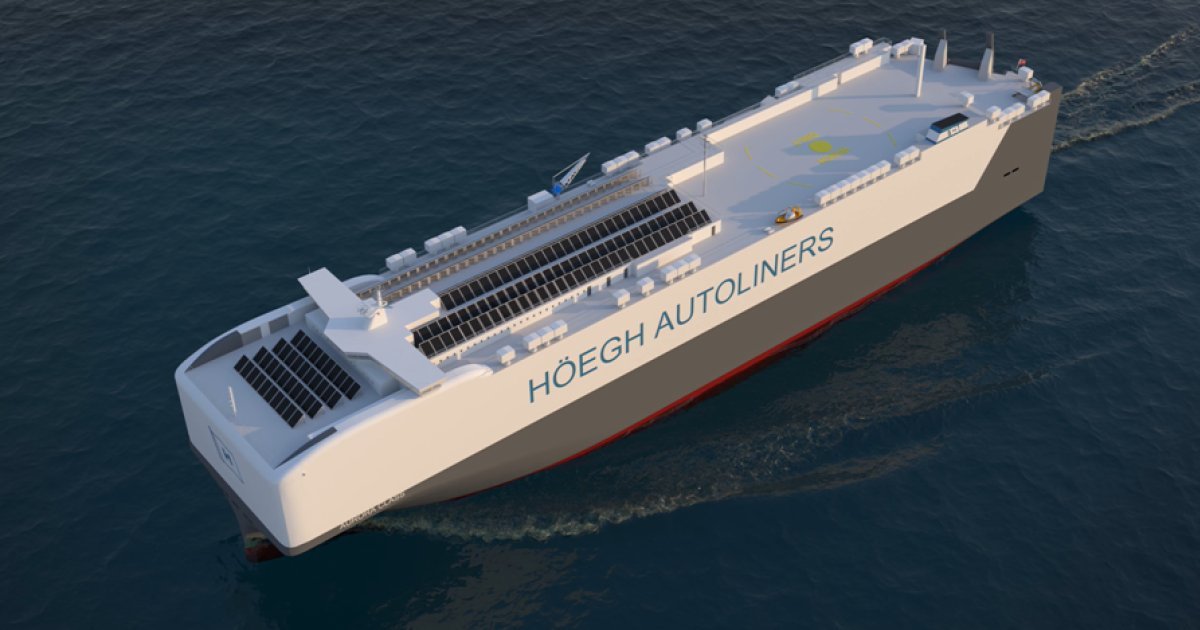

Next Generation of Vessels
Converting boxships to methanol & ammonia is feasible and cost-effective, report says: Converting containership vessels to alternative fuels is technically and economically feasible, Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping said citing findings of a new report.
As the industry moves to decarbonize its fleet, numerous questions remain to be answered on the best pathways for shipowners given the uncertainty in relation to the future fuel landscape.
The report takes a deep dive into the technical, environmental, and techno-economic impacts of preparing container ships for conversion to green fuels to de-risk investment decisions and provide shipowners with answers on what converting boxships to ammonia or methanol would entail.
DSME, ABS chart decarbonization path for ship designs: American Burea of Shipping (ABS) and South Korea’s shipbuilder Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME) have formed a joint development project to create a decarbonization strategy for DSME’s LNG carrier designs.
Signed at Gastech, the project will see ABS and DSME investigate carbon emission performance of ships in various segments. Specialists from ABS’ Simulation Center in Singapore will then simulate the performance of a range of decarbonization technologies. The outcomes of the JDP will allow DSME to compare and select the best decarbonization options for each specific ship segment.
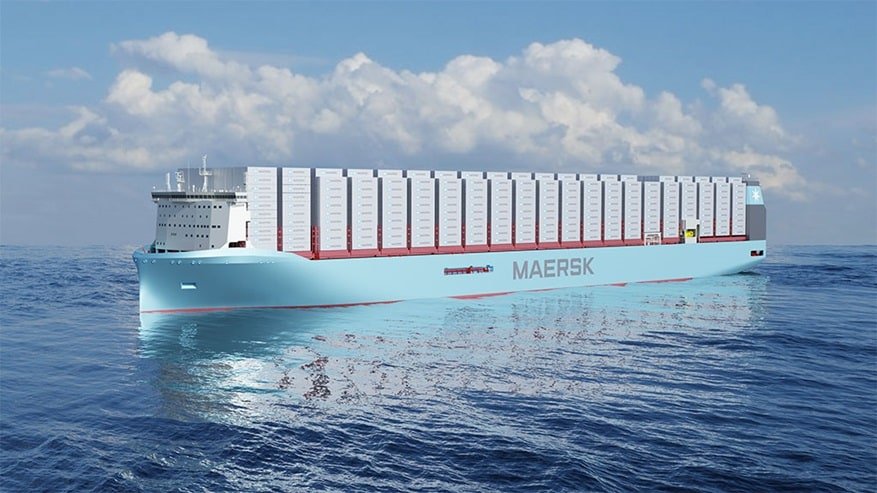
Maersk books six more methanol-fuelled boxships at HHI: The six vessels will be built by South Korean shipbuilder Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI) and have a nominal capacity of approx. 17,000 TEU. They come with dual-fuel engines able to operate on green methanol which is expected to save about 800,000 tons of CO2 emissions annually. The six 17,000 TEU vessels are all to be delivered in 2025 and will sail under the flag of Denmark.
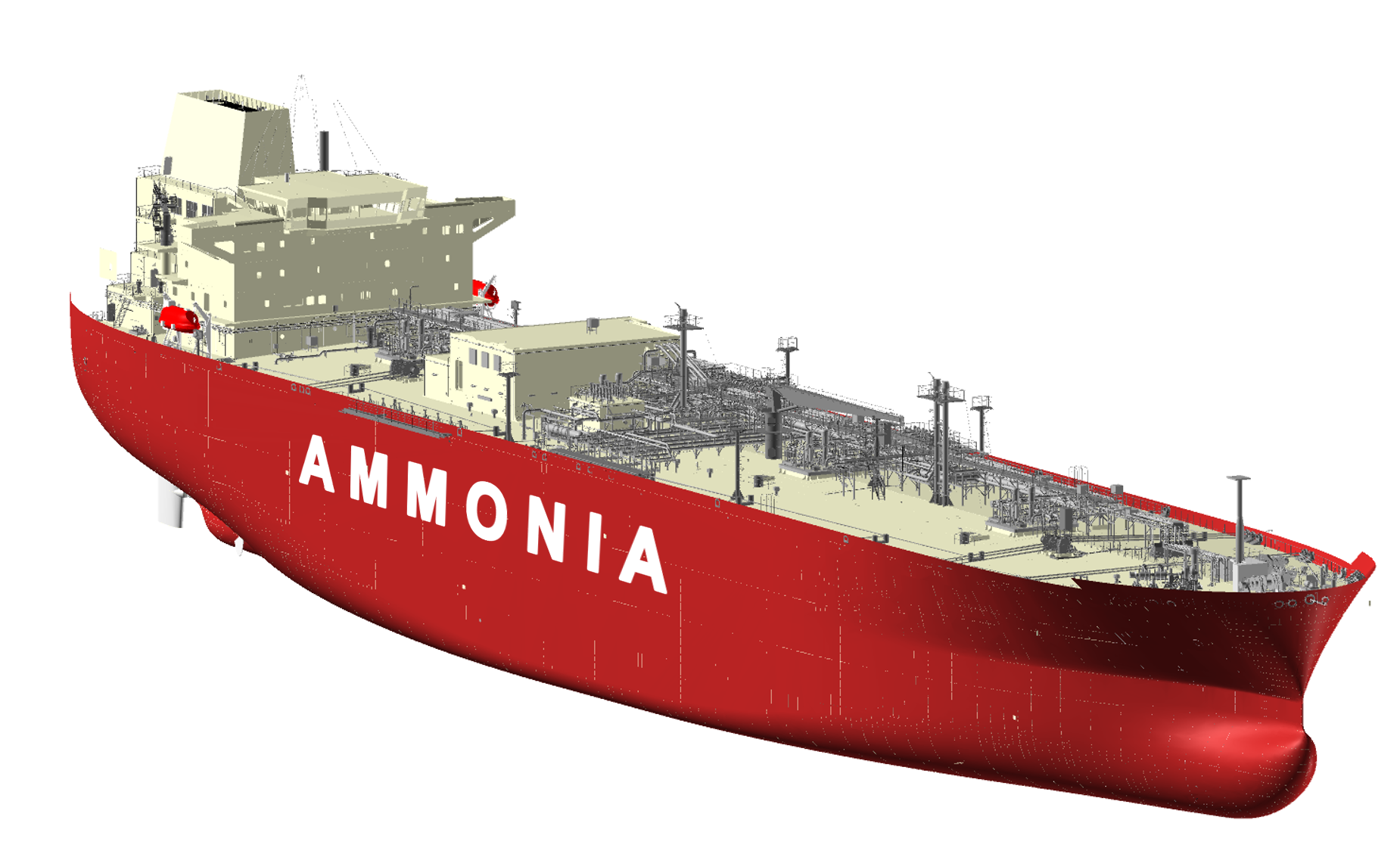
 BV grants AiP to DSME ammonia-fuelled very large ammonia carrier:
BV grants AiP to DSME ammonia-fuelled very large ammonia carrier: The vessel design is 230 m in length, 36.6 m wide, and 22.5 m tall and will have four prismatic-type cargo tanks with a combined carrying capacity of 86,000 cu m. Ammonia has the potential to be a zero-carbon fuel in the maritime industry. Despite the challenges, some 71 vessels on order were noted as ammonia-ready in a recent Clarksons Research study. LNG remains the leader in alternative fuels for vessels on order, followed by battery/hybrid, albeit for smaller vessels.
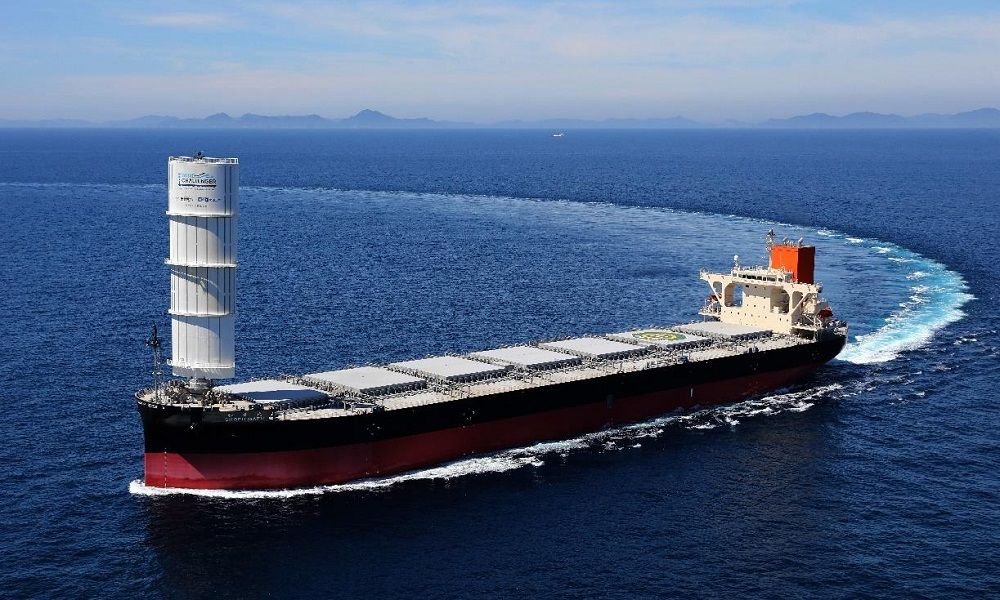
 MOL’s wind-assisted bulk carrier enters service:
MOL’s wind-assisted bulk carrier enters service: Mitsui OSK Lines (MOL)’s bulk carrier equipped with a hard sail wind power propulsion system has officially started operation following a handover ceremony at Oshima Shipbuilding. The 98,700 dwt bulker, named Shofu Maru, is the first wind-assisted newbuild for the Japanese owner that sports a telescoping hard sail developed in-house in collaboration with compatriot shipbuilder Oshima under the Wind Challenger project. The additional propulsion power from wind is expected to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by about 5% on a Japan-Australia voyage and about 8% on a Japan-North America West Coast voyage, compared to a conventional vessel of the same type, and contribute to curbing GHG emissions during fuel transportation, MOL said in a statement.




















 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 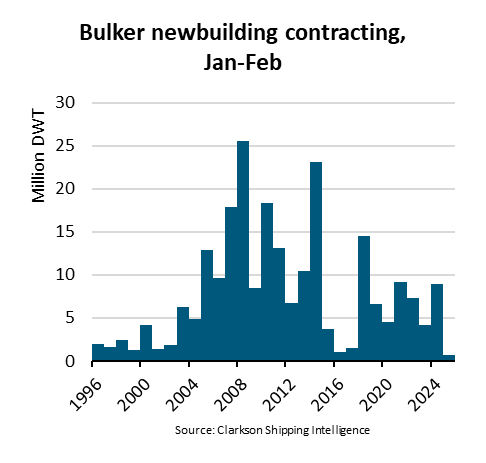 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar