Following the announcement of six strategic green methanol partnerships across the globe earlier this year, A.P. Moller-Maersk (Maersk) has added a seventh methanol partnership with Chinese bioenergy enterprise Debo on the quest to boost global production capacity. The parties have signed a Letter of Intent covering Debo's plans to develop a bio-methanol project for Maersk in China with a capacity of 200,00t/yr to start commercial operation by autumn 2024. Maersk has set an ambitious end-to-end net-zero goal for 2040 and the availability of green methanol at scale is critical to its fleet's transition to sustainable energy. Partnerships across ecosystems and geographies are essential for the scale-up needed to make meaningful progress on this agenda in this decade.
India's first indigenous hydrogen-fuelled electric vessel to arrive next year: India's first indigenously built hydrogen-fuelled electric vessel is planned to be delivered by March/April 2023, Asian News International (ANI) reported, citing Madhu S Nair, Chairman and Managing Director of Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL). Back in April this year, the country's Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways announced the innovative project, kick-starting India's efforts towards green shipping. The ship in question will be a hydrogen-powered fuel cell passenger ferry.

TECHNOLOGY
GT Green Technologies, PEI TECH LLC join hands on wind propulsion tech: UK-based wind propulsion expert GT Green Technologies has teamed up with PEI TECH LLC, a marine industry company from Texas, to work on advanced wind propulsion technology.
GT Green Technologies has developed a wingsail that incorporates novel air-flow technology, which provides an ‘unparalleled amount of thrust per unit size’ while maintaining a low stowage profile when not in use. The technology is patent-pending, based on the company's website. The technology promises to save operators between 10 to 30 percent in fuel consumption for retrofitted ships and up to 50 percent for newbuilds. The devices are modular and retrofittable above deck.
ABS launches nuclear propulsion study: The US Department of Energy (DOE) has awarded class society ABS a contract to research barriers to the adoption of advanced nuclear propulsion on commercial vessels. The $800,000 research project will address challenges to adopting new reactor technology in commercial maritime applications at a time when a host of companies around the world are looking to commercialize atomic propulsion. ABS will develop models of different advanced reactor technologies for maritime applications and develop an industry advisory on the commercial use of modern nuclear power.
Norsepower to install rotor sails onboard two new-built CO2 carriers: Norsepower has inked a contract with Dalian Shipbuilding Industry to deliver single rotor sails onboard two new-built LNG-powered, wind-assisted CO₂ carriers commissioned by the Northern Lights JV. Northern Lights JV is developing the transportation and storage component of Norway's Longship project to decarbonize industrial emissions. The two liquified CO₂ carriers will be equipped with one 28x4m Norsepower rotor sail on each vessel. The wind propulsion developer estimates that the sails will reduce the fuel and CO₂ emissions from each vessel by approximately 5%.
Still room for improvement in the propulsive efficiency of ships: There is significant room for improvement in the propulsive efficiency of ships with new propulsor and hull form innovations to help reduce fuel consumption and add to the decarbonization efforts of the shipping industry, Finland-based research institute VTT said. Propulsive efficiency translates to the amount of power delivered to the propeller that can be used for propelling a ship. Now it stands around 70 percent. This kind of improvement is not dependent on fuel types, according to VTT, which claims that the discussion around decarbonizing shipping has been largely focused on future fuel types such as ammonia and hydrogen. The institute is currently engaged in a project on developing new methods to model underwater noise, a major environmental issue in the shipping industry, and propeller cavitation phenomena. By better understanding the sources of the underwater noise, it can be mitigated more effectively.

FUELS
1st LNG-fuelled tanker joins Anglo-Eastern's managed fleet: MT Proteus Jessica, a 110,000 DWT tanker, has been delivered to Anglo-Eastern's managed fleet, becoming the company's first dual-fuel LNG-powered tanker. The LR2 tanker was built by China's Shanghai Waigaoqiao Shipbuilding and was delivered in June 2022. Anglo-Eastern is also working with industry partners on a joint study framework to discuss common issues in the utilization of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel. These include safety assessments of NH3 as fuel, it's bunkering, and CO2 emission at NH3 production.
Jurong Port, Jera, and Mitsui forge a partnership on ammonia production: Jurong Port, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Asia Pacific (MHI-AP), a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and JERA Asia, a subsidiary of JERA have teamed up on the production of ammonia. The trio has entered a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to explore establishing a 100% ammonia direct combustion power plant on Jurong Island, Singapore, which houses the country's chemical and energy industries.
Under the MoU, a joint study will be conducted, where a 60MW class gas turbine combined cycle plant fueled by 100% ammonia is planned to be set up to produce carbon-neutral electricity, as well as stimulate ammonia demand to be ready for ammonia bunkering in future.
Anaergia to supply biogenic CO2 to European Energy for e-methanol production as fuel for Maersk ships: Canada-based clean energy producer Anaergia has signed an agreement with Denmark's wind and solar energy producer European Energy for the supply of liquefied biogenic carbon dioxide (CO2). Under the terms of this agreement, Anaergia is to supply European Energy with up to 60,000 tonnes per year of liquefied biogenic CO2 for a period of 10 years. Biogenic carbon dioxide is carbon dioxide that is released during the decomposition of organic matter such as food waste. All Anaergia plants use organic waste material to produce biogas, which is composed of methane and carbon dioxide.
Pasha Hawaii's new boxship 1st to refuel with LNG on U.S. West Coast: Pasha Hawaii's MV George III has become the first container ship powered by liquefied natural gas (LNG) to refuel on the U.S. West Coast. On 17 August 2022, the US Port of Long Beach welcomed the new build. Delivered last month, MV George III is the first of two Ohana-class vessels to join Pasha Hawaii's fleet. It will be serving the Hawaii/Mainland trade lane.

PORTS
Jordan's ACT joins the 2040 net zero club: Aqaba Container Terminal (ACT), Jordan's only container port and the sustainable gateway to the Levant region and beyond, has announced the launch of a decarbonization strategy that is set to reduce its carbon footprint to net zero by 2040. ACT is committed to reducing its total emissions by 70 percent between 2020 and 2030. The company's long-term target is to reach net-zero emissions by 2040. This objective is being supported by a CAPEX plan that will devote more than $50 million in incremental investments over the next 20 years toward decarbonization projects. This plan is divided into four major initiatives — energy optimization, civil work, expansion of on-site solar installations, and a green premium on electrified equipment, including electrical chargers.
PortsToronto renews green energy commitment: Canadian port authority PortsToronto has renewed its agreement with domestic green energy provider Bullfrog Power Canada to power all of its operations with green energy. The new agreement runs until 31 July 2026. Since 2010, PortsToronto has reduced its environmental footprint by choosing 100 percent green energy to power all of its operations with clean, renewable electricity – the only port authority and airport in Canada to do so.
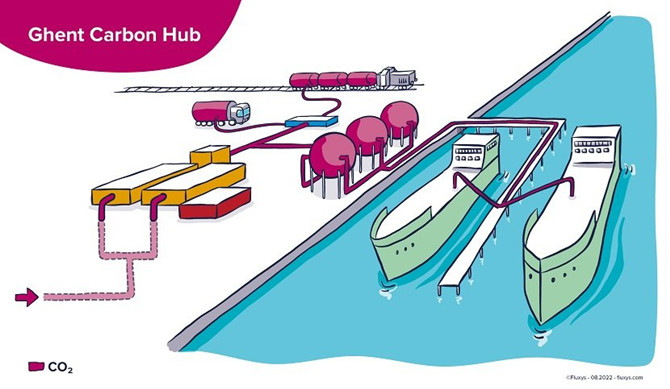
North Sea Port could become CO2 storage and liquefaction hub: Belgian energy infrastructure group Fluxys, steel and mining company ArcelorMittal Belgium and North Sea Port have started a feasibility study for the Ghent Carbon Hub project, an open-access CO2 storage and liquefaction hub in the Ghent part of North Sea Port. Besides the use of carbon-neutral energy, carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) is essential for CO2-intensive industries to achieve net zero emissions, especially in hard-to-abate sectors with processes inherently generating CO2 emissions. The three partners are pressing ahead to develop a key infrastructure accommodating the CCUS chain.
GOVERNMENT
Germany allocates €30 million per year for zero-emission vessels: Germany's government has unveiled its decision to allocate millions of euros for the development of zero-emission vessels and support digitization in shipbuilding. On 18 August 2022, Claudia Müller, Federal Government Coordinator for the Maritime Industry and Tourism, handed over the grant agreement in the amount of €1.3 million ($1.3 million) to the consortium for the digitization of shipbuilding under the direction of Ostseestaal GmbH. As explained, the goal is to make shipbuilding smarter, more cost-efficient, and sustainable. This will be achieved by creating digital product models in which the entire process of a ship's lifecycle can be mapped.

By Maria Bertzeletou, Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com









 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 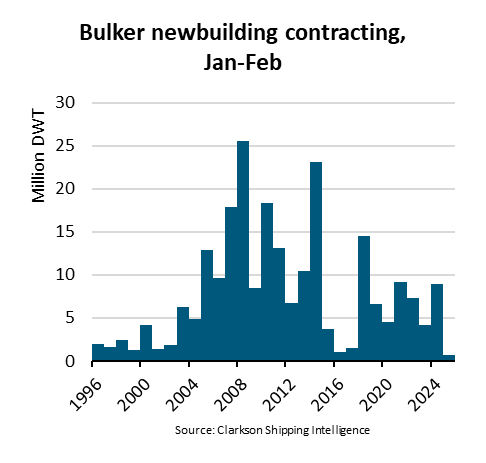 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar