Essentially, Blue Visby uses digital technology to optimize and stagger arrival times for groups of vessels traveling to the same port, with an algorithm providing an optimal arrival time for each vessel. This enables ships to slow down, cutting their fuel consumption and emissions, but still keep their place in the queue and arrive one after the other, which reduces unnecessary waiting times outside ports. The mechanism enables stakeholders on each voyage including shipowners, charterers, and cargo interests to share the costs and benefits of the implementation of the Blue Visby Solution, including fuel savings, the costs of a lengthier journey, and the financial value of emissions reductions where applicable.
The Danish tanker shipping firm Maersk Tankers, together with shipowners in its pools, has launched a new digital solution to help owners meet the required marine emissions standards. Using the new solution, which has been developed together with shipowners in the company’s pools, owners can monitor their vessel’s rating, how it changes year by year, the reasons for any changes, and its projected rating over the following three years.
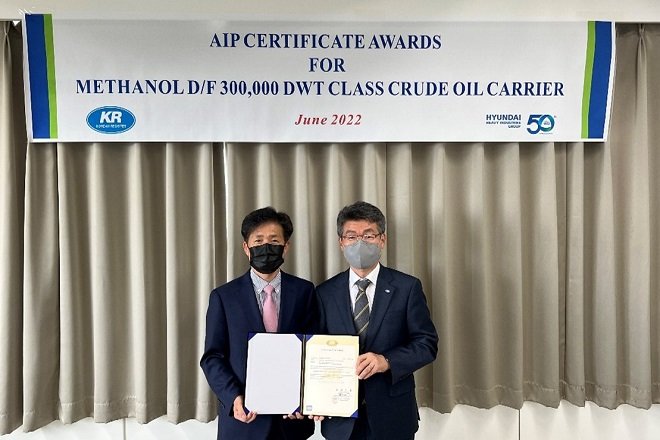
Methanol dual-fuel VLCC design wins KR approval: A methanol dual fuel 300,000 dwt very large crude oil carrier (VLCC) has received approval in principle (AIP) from the classification society Korean Register (KR). The methanol dual-fuel VLCC, which was developed under a joint project between KR and Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI), is powered by methanol and marine gas oil (MGO). HHI has developed the vessel so that the methanol fuel tank can be placed in either the open deck or the cargo area and KR has verified the safety and suitability of the vessel’s design, ensuring it complies with domestic and international regulations.
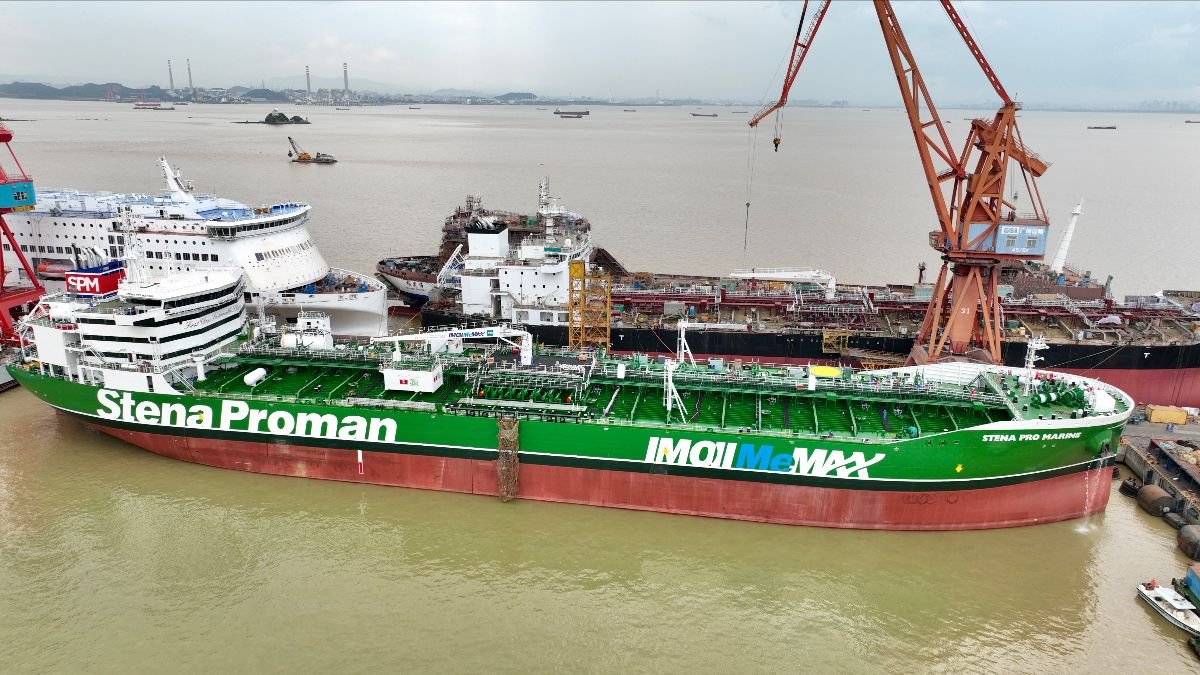
 Proman Stena Bulk welcomes the second methanol-fuelled tanker:
Proman Stena Bulk welcomes the second methanol-fuelled tanker: Shipping joint venture Proman Stena Bulk has accepted delivery of the second methanol-powered newbuild tanker, Stena Pro Marine. Both IMOIIMeMAX dual-fuel mid-range (MR) tankers were built at Guangzhou Shipyard International Co Ltd (GSI) in China. Stena Pro Marine, like Stena Pro Patria, is expected to consume 12,500 tonnes of methanol per annum. The use of methanol onboard virtually eliminates local pollutants including SOx and Particulate Matter (PM), cuts NOx emissions by 60%, and reduces CO2 emissions by up to 15% versus conventional marine fuels.
 PIL signs up for additional dual-fuel ammonia-ready boxships:
PIL signs up for additional dual-fuel ammonia-ready boxships: Seeing liquefied natural gas (LNG) as a commercially viable fuel solution, Singapore-based shipping company Pacific International Lines (PIL) has placed an order for four 8,000 TEU LNG dual-fuel container vessels. The company said it awarded a contract to the Chinese shipyard Yangzijiang Shipbuilding for the construction of four vessels that will be delivered progressively in 2025. According to PIL, the newly ordered vessels will be equipped with an ammonia intermediate-ready fuel tank.

Topeka, the Wilhelmsen owned zero emission shipping company, launches two carbon neutral, methanol fuelled container newbuilds: The two new-build ships will replace three of North Sea Container Line's (NCL) current diesel-powered vessels, which will be phased out of operations. Technical management will be done by Wilhelmsen Ahrenkiel Ship Management, making them one of the first ship managers to gain experience and competence in the use of methanol as fuel on container ships.
By using the best available technology, Topeka's ambition is to decarbonize shipping. The two new vessels will run on methanol, which is regarded as the best solution, in this case, carrying heavy loads along the Norwegian coast and onward to the European continent, covering 3000 nautical miles with 18 000 deadweight tons. With green methanol, the two vessels offer a carbon-neutral logistic solution from Norway to the European market.

MPC Capital further expands its commitment to the decarbonization of the shipping industry: Hamburg-based asset and investment manager MPC Capital has initiated a project to build two new container ships powered by climate neutral (“green”) methanol. The project was developed in cooperation with the Norwegian Wilhelmsen group and is part of a series of activities by MPC Capital to decarbonize the maritime sector.
The vessels have a total investment volume of USD 78 million and a capacity of 1,300 standard containers (TEU) each. With their modern design and the most advanced propulsion technology based on green methanol, the vessels are among the first container ships to already comply with all the measures launched by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to reduce emissions in shipping. The two ships are being built in China – with key technologies from Europe – and are scheduled for delivery in 2024.
Cruise Sector / Ferries
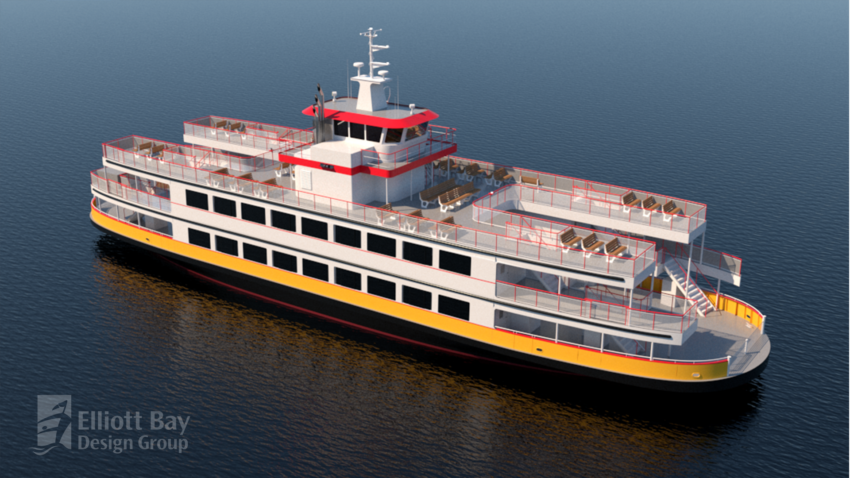
Casco Bay hybrid-electric ferry enters construction phase: Hybrid-electric passenger vehicle ferry, designed by the US naval architect Elliott Bay Design Group (EBDG) for Maine ferry operator Casco Bay Lines, is entering the construction phase at Senesco Marine shipyard at Rhone Island. The hybrid-electric 50-metre ferry will replace an existing diesel-powered ferry, reducing 800 tons of CO2 each year and improving air quality in and around Portland, Maine. The contract design meets operational requirements, increased passenger demand, and the operator’s goal of reducing its carbon footprint.
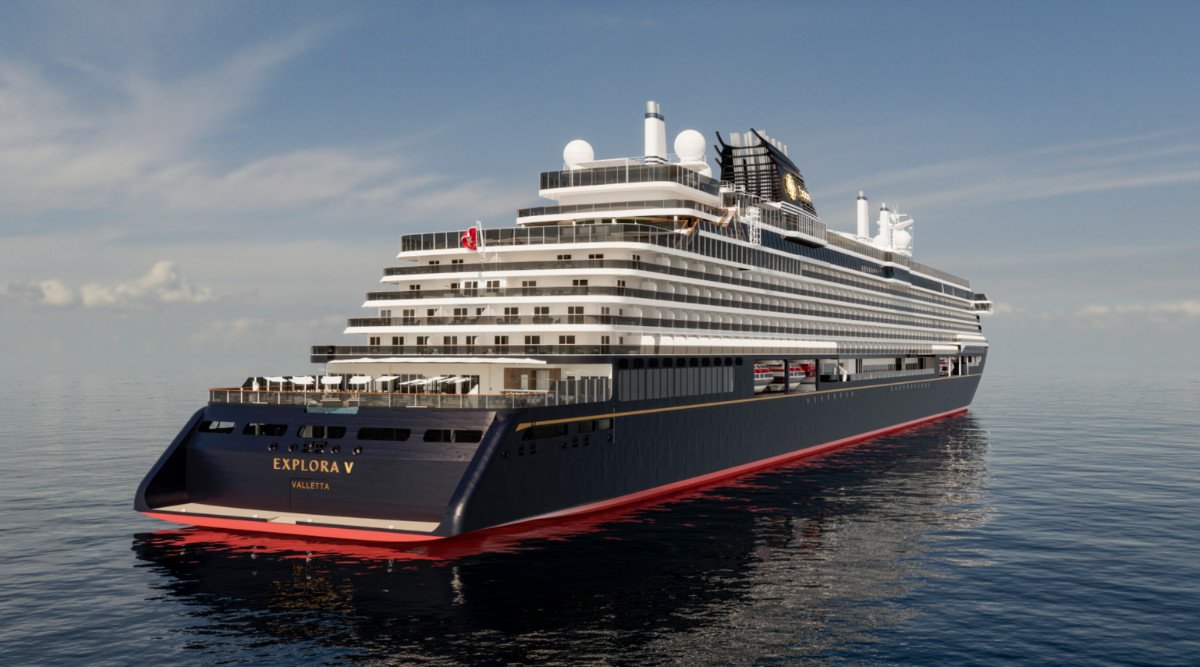
 MSC orders two next-gen hydrogen-powered cruise ships in Italy:
MSC orders two next-gen hydrogen-powered cruise ships in Italy: Explora Journeys, the luxury travel brand of the MSC Group's cruise division, and Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri have signed a memorandum of agreement (MOA) for the construction of an additional two hydrogen-powered cruise ships to take the total fleet number from four to six vessels. EXPLORA V and VI will feature a new generation of liquefied natural gas (LNG) engines that will tackle the issue of methane slip and will also be equipped with industry-first environmental technologies and solutions, including a containment system for liquid hydrogen that will enable them to use this promising low-carbon fuel.

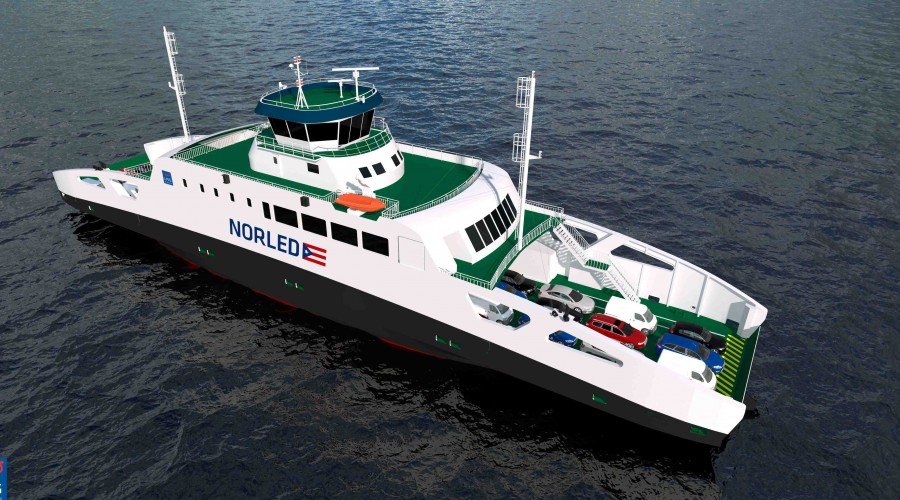
Sembcorp Marine hands over 2nd zero-emission battery-powered RoPax to Norled: Built based on the proprietary design of Sembcorp Marine's wholly-owned subsidiary, LMG Marin AS, the zero-emission vessel will be capable of operating at a service speed of 10 knots, powered by lithium-ion batteries which are charged using green hydro-electric power.
The ferry can also run on a combined battery-diesel hybrid backup mode when required. Optimized to meet Norled's operational requirements, the ferry named Dragsvik is equipped with energy-efficient features including quick-connection shore charging plugs, auto-mooring, auto-cross capabilities, efficient hull, propulsion, and heat recovery systems.

TECO 2030 gets funding to develop hydrogen-powered high-speed vessels: A consortium led by Norwegian cleantech company TECO 2030, compatriot shipbuilder Umoe Mandal and maritime engineering company BLOM Maritime is developing a hydrogen-powered high-speed vessel with zero emissions under the “High-speed vessel of the future” project. Under the project, the county municipalities of Finnmark, Nordland, Trøndelag and Vestland aim to develop groundbreaking technology in several areas and one of them is to develop, build and demonstrate the world's first hydrogen-powered high-speed vessel.
As described, the contract contains two phases, where the consortia will first develop and get their solutions approved in 2022 and 2023.
In the next phase, one supplier will be chosen to build and demonstrate the newly developed vessel. The vessel will be in pilot operation from 2025. The vessel will combine fuel cell systems from TECO 2030 and an energy-efficient catamaran design with Surface Effect Ship (SES) technology from Umoe Mandal. It will be able to transport 200-300 passengers at speeds above 35 knots while sailing over long distances.

Fuels
ClassNK releases “Guidelines for Ships Using Alternative Fuels (Edition2.0)” -adding specific safety requirements for ammonia-fueled ships: ClassNK has released the “Guidelines for Ships Using Alternative Fuels (Edtion 2.0),” which sets forth safety requirements for ships fueled by methanol, ethanol, LPG, and ammonia. In particular, specific requirements for ammonia-fueled ships have been added to provide guidance for the design of alternative-fueled ships.
These guidelines comprehensively describe safety requirements for methanol, ethanol, and ammonia-fueled ships. Taking into account the risks posed by the use of alternative fuels against ships, crews, and the environment, they specify requirements for installation, controls, and safety devices to minimize those risks.
Singapore-based shipowner Eastern Pacific Shipping (EPS) has completed the first LNG bunkering operation: The supply of 1,500mt of LNG took place at the Port of Pengerang in Malaysia on 4 July 2022 following the vessel's delivery from China's Guangzhou Shipyard International Company Limited on 28 June 2022. According to EPS, the delivery and LNG bunkering was completed with support from various industry partners, including marine fuel supplier, Peninsula, which partnered with Petronas Marine to perform the LNG bunker supply.
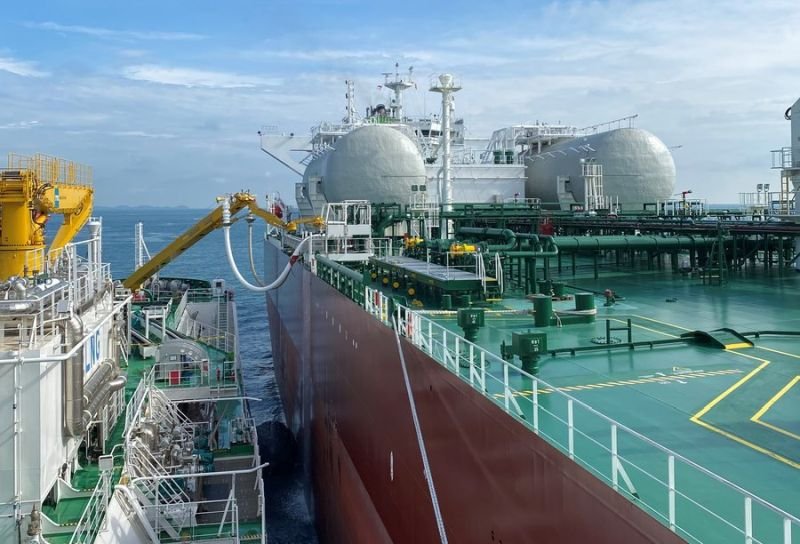

DNV approves Vale's multi-fuel tank design in a ‘major’ advance for low-carbon fuels adoption: Brazilian mining company Vale has received approval in principle from the classification society DNV for its design incorporating multi-fuel tanks on iron ore carriers, developed because of the project seeking to adopt alternative, lower-carbon fuels for shipping.
DNV performed an independent assessment of the design to verify its technical feasibility, indicating that, based on this system, vessels chartered by the mining company could be adapted to store fuels such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, and ammonia in the future. According to Vale, the design, which was developed in partnership with Norwegian companies Brevik Engineering AS and Passer Marine, represents a major advance in the adoption of low-carbon fuels in the shipping industry.
Biofuels
Hapag-Lloyd to use advanced biofuels for transport of DHL shipments: DHL Global Forwarding, the air and ocean freight specialist of Germany's Deutsche Post DHL Group, has signed an agreement with compatriot liner shipping company Hapag-Lloyd for the use of advanced biofuels. As an initial step, Hapag-Lloyd will ship 18,000 TEU of DHL's volume using advanced biofuels, which is equivalent to a reduction of 14,000 tons of Well-to-Wake CO2-emissions. The two companies share the vision of decarbonizing container shipping and logistics. With their project, they demonstrate the scalability of sustainable transport solutions and the relevance of sustainable fuels in today's market.

Regulations
EU port and terminal operators call for a focused approach to shore power in AFIR and FuelEU Maritime: Representative bodies of the EU port authorities and terminal operators, the European Sea Ports Organisation (ESPO) and the Federation of European Private Port Companies and Terminals (FEPORT) have jointly agreed that the proposals for an Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) and the FuelEU Maritime Regulation should enable the deployment of onshore power supply (OPS) where it makes the most sense.
According to the organizations, the greening of shipping entails addressing emissions from shipping both during navigation and at the berth and onshore power supply is one of the technologies that can help reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions at the berth.
World's largest ocean carrier MSC signs UN Sustainable Ocean Principles: Swiss Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC), the world's largest ocean carrier by operated container vessel capacity, has joined over 150 stakeholders in signing on to the UN Global Compact Sustainable Ocean Principles. Building on and supplementing the Ten Principles of the UN Global Compact on human rights, labour, environment, and anti-corruption, the Sustainable Ocean Principles provide a framework for responsible business practices across ocean sectors and geographies covering ocean health and productivity, and governance and engagement and data and transparency.
Ports
Ports of Duisburg and Amsterdam to jointly develop hydrogen value chain: As part of the cooperation, the ports of Amsterdam and Duisburg will jointly explore the potential of several hydrogen carrier technologies, with the aim of establishing an international supply chain for hydrogen on a commercial scale. It is believed that the import, storage, and distribution of green hydrogen carriers play an instrumental role in enabling the energy transition in the industrial and maritime sectors. The Port of Amsterdam is part of the H2A consortium, which aims to import one million tons of green hydrogen to the port and includes multiple significant players in the hydrogen industry.

Source: Maria Bertzeletou, Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com

















 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 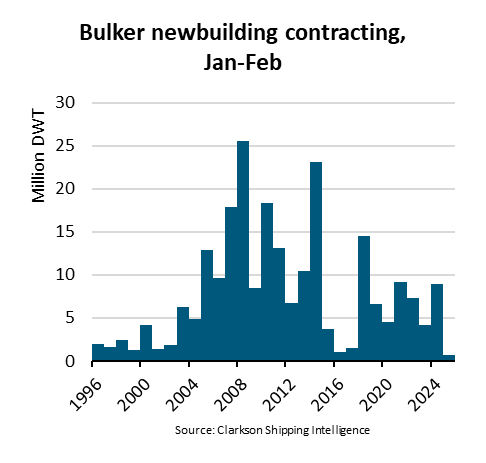 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar