From the air base of Sarzana, the Italian Coast Guard has been deploying EMSA's remotely piloted aircraft to gain increased maritime awareness over the Gulf of Genoa since 16 June. The flights are being used to enhance general maritime safety and security, as well as to assist in search and rescue missions. Protection of the marine environment is another important aspect of the operation and flights will be used to monitor whale migration within the Pelagos Sanctuary, a protected area for marine mammals.

This multipurpose operation allows the Italian Coast Guard to assess how remotely piloted aircraft can be deployed as part of their standard operating procedures to provide enhanced situational awareness. This will be particularly useful for monitoring whale migration and merchant vessels transiting the protected marine area of the Santuario dei Cetacei or Pelagos Sanctuary, located between the French and Italian coastlines. By using the EMSA RPAS data centre, the flights can be directed and followed remotely from six locations including the Sarzana airbase, Imperia, Savona, La Spezia, Genoa and Rome.
The aircraft being used is an AR-5 Evo unmanned fixed wing aircraft and it is under contract to EMSA from the REACT consortium, comprising the companies CLS and Tekever. It can fly more than 10 hours and beyond radio line of sight using satellite communications. It has several features making it suitable for performing both day and night operations including optical and infrared cameras, a maritime radar, an AIS receiver and an emergency position-indicating radiobeacon (EPIRB) antenna. The aircraft can also be equipped with an inflatable life raft for eight persons to be dropped in support of Search and Rescue operations.
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com


 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 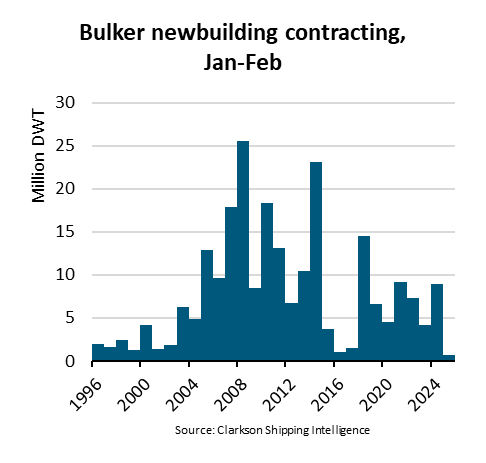 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar