Latest Trends on fuel transition, shipyard actions, government, ports, financing and industry players
In the meantime, the United States and Norway are launching a Green Shipping Challenge for COP 27. This initiative encourages governments, ports, maritime carriers, cargo owners, and others in the shipping value chain to come forward with concrete steps that will help put the international shipping sector on a credible pathway this decade toward full decarbonization no later than 2050. These could include, for example, steps to produce zero-emission fuels; develop zero-emission bunkering and recharging capabilities; deploy low- or zero-emission vessels, and create, or provide financial and technical support for green shipping corridors. President Biden invited the leaders to express their support for the Green Shipping Challenge and to announce specific actions under the initiative at COP 27.
Equinor comes on board Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center in the push to speed up shipping decarbonization: Norwegian state-owned energy giant Equinor has joined the Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping, a nonprofit, independent R&D center, on its journey to accelerate and boost the decarbonization of the shipping industry. As part of its goal “to take a leading role in the energy transition,” Equinor has set its sails on “a journey to net-zero emissions,” which the Norwegian giant intends to achieve by optimizing its oil and gas portfolio, accelerating growth in renewables, carbon capture, and hydrogen. They committed to a long-term strategic collaboration and contribution to the development of zero-carbon technologies and solutions for the maritime industry.
 Scotland, Germany launch a green hydrogen partnership:
Scotland, Germany launch a green hydrogen partnership: Germany's largest state Bavaria and Scotland have decided to strengthen ties in the field of green hydrogen and explore the potential of its transportation. On 13 June, Hubert Aiwanger, Bavaria's Economics and Energy Minister, and Ivan McKee, Scottish Minister for Economy, Trade, and Tourism, signed a letter of intent in Glasgow to expand their existing business-scientific cooperation with green hydrogen.
 ABS, Arcsilea exploring IMO's decarbonization measures:
ABS, Arcsilea exploring IMO's decarbonization measures: A consortium between by U.S. classification society American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) and U.K.'s consultancy provider Arcsilea has won a tender from the European Commission to carry out a technical study on the future of ship energy efficiency measures introduced by the International Maritime Organization (IMO). As disclosed, the partners won the tender from the European Commission's Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport (DG MOVE). The 15-month-long project will analyze the IMO's Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII), Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI), and Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) framework. Moreover, the parties will provide recommendations for further development, effective implementation, and enforcement.

TotalEnergies buying a stake in Adani to bring forth the ‘largest green hydrogen ecosystem in the world’: French energy giant TotalEnergies has inked a deal to acquire a stake in a subsidiary of Adani Enterprises Limited (AEL), which will enable it to further pursue its low carbon hydrogen strategy while joining forces with AEL to produce and commercialize green hydrogen in India. Since TotalEnergies is convinced that renewable and low-carbon hydrogen will play “a major role in the energy transition,” the French player is working with its suppliers and partners to decarbonize all the hydrogen used in its European refineries by 2030. Once accomplished, this will represent a reduction in CO2 emissions of 3 million tons per year.
Sea Cargo Charter, industry giants disclose the climate impact of their shipping activities: Some of the world's largest energy, agriculture, mining, and commodity trading companies publish the climate alignment of their shipping activities and gain access to new data that will allow them to work with their business partners in driving carbon efficiency and reductions and align their chartering activities with climate action goals. Signatories to the charter commit to measuring and publicly disclosing the alignment of their chartering activities with the ambition to reduce total GHG emissions from international shipping by at least 50% by 2050, as set out by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
The signatories reporting this year are ADM, Anglo American, Bunge, Cargill, COFCO International, Copenhagen Commercial Platform (CCP), Diamond Bulk Carriers, Dow, Eagle Bulk, Enviva, Equinor, Gunvor, Holcim Trading, Klaveness Combination Carriers, Louis Dreyfus Company, Maersk Tankers, Norden, Nova Marine, NYK Bulkship (Atlantic), Shell, Signal Maritime Services, Tata Steel, Torvald Klaveness, TotalEnergies, and Trafigura.

Cruise Sector
Costa Group to bolster net-zero targets with new decarbonization department: Cruise company Costa Group, a part of Carnival Corporation, has established a dedicated decarbonization department within its Carnival Maritime unit based in Hamburg. As informed, the newly established department will be responsible for developing and implementing the strategy for achieving the decarbonization ambitions of the Costa Cruises and AIDA Cruises fleets by 2050. Furthermore, the effort will have a strong focus on research and development, energy management, and data analytics to develop the roadmap that will lead to zero-emission ship operations.
Construction starts on TUI Cruises' methanol-ready cruise ship: Finnish shipbuilding company Meyer Turku has held a steel-cutting ceremony for Mein Schiff 7, the latest cruise ship to be built for German TUI Cruises, a joint venture between TUI and Royal Caribbean Group. The Mein Schiff 7 is an important milestone in the company's efforts to provide the first climate-neutral cruises by 2030. TUI plans to grow the Mein Schiff fleet to nine ships by 2026. The company has also signed a contract with Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri to build two new liquefied natural gas (LNG) powered ships.

Technology
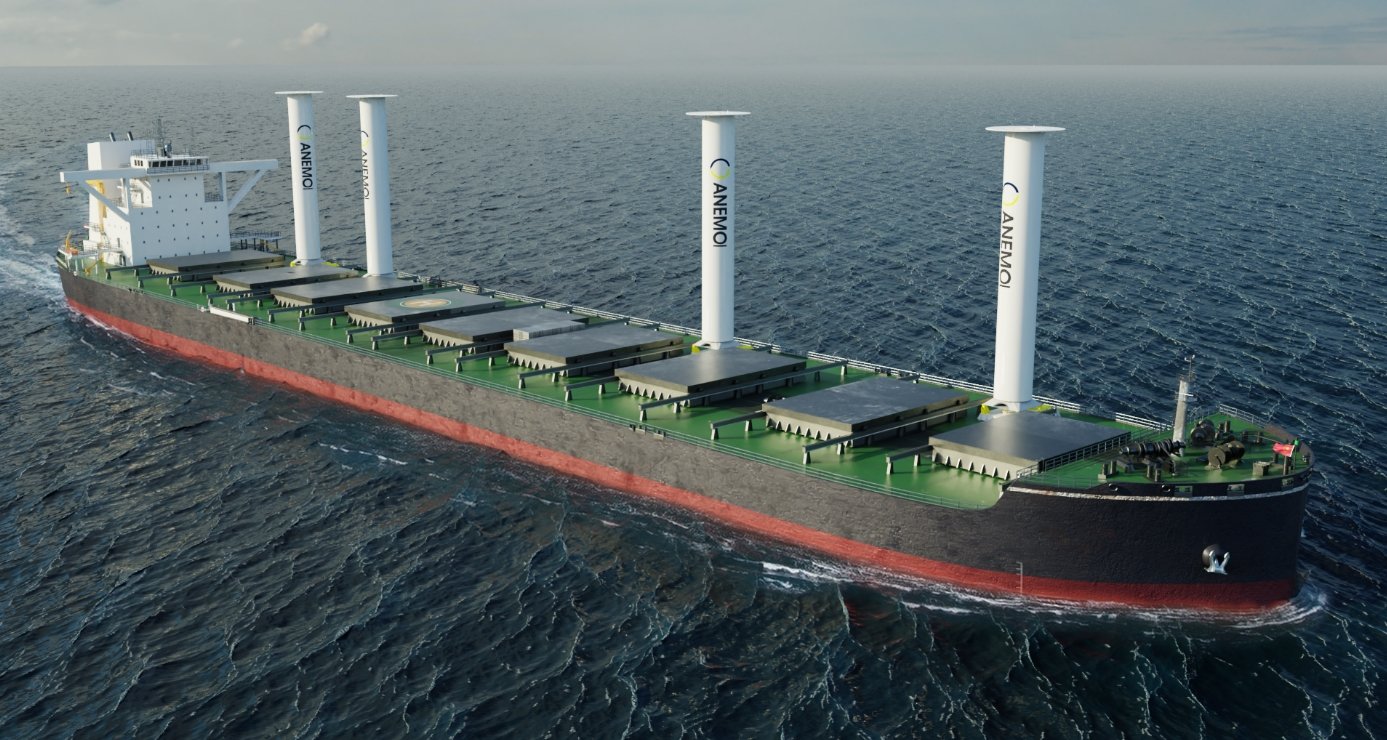
Study validates significant EEDI reduction with rotor sails on bulker: A joint research project focusing on enhancing the performance of large cargo vessels is reporting a significant energy reduction resulting in the awarding of its first Approval in Principle from Lloyd's Register. Launched in 2020, the project is bringing together naval architects with the OEM, ship owner, and classification society to develop a series of energy-efficient vessel designs incorporating rotor sails. The first project focused on a 210,000 dwt Newcastlemax bulk carrier from Oldendorff Carriers as the shipowner. They studied installing Anemoi Rotor Sails on a new build significantly improves efficiency and reduces environmental impact.
 WinGD, HHI to jointly develop ammonia two-stroke engine:
WinGD, HHI to jointly develop ammonia two-stroke engine: Swiss engine developer WinGD and Engine Machinery Division (EMD) of the South Korean shipbuilder Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI) have decided to collaborate on delivering the first WinGD engine capable of running on ammonia. Through this collaboration, the partners aim to provide ‘a vital step’ in shipping's progress towards decarbonization. The project will explore ammonia concepts for both diesel-fuelled WinGD X-type engines and dual-fuel LNG X-DF engines.
Next Generation of Vessels
TECO 2030 and partners launch hydrogen tanker concept: Norwegian cleantech company TECO 2030 has introduced a hydrogen-powered tanker concept, Hy-Ekotank, together with its partners Ektank AB, Shell Shipping, Maritime, and DNV. The hydrogen-powered tanker will allow zero emissions at berth, and up to 100% reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions during the voyage, according to TECO 2030. This pioneering concept could become a first mover in this maritime shipping segment and contribute to the development of achieving the ambitious climate targets committed by the European Union.
 Breeze to design ammonia-fueled gas carrier for NoGAPS project:
Breeze to design ammonia-fueled gas carrier for NoGAPS project: The Norwegian ship design company has entered into an agreement with Nordic Green Ammonia Powered Ships (NoGAPS) project consortium to conduct feasibility studies and develop the concept design for the ammonia-fueled gas carrier MS NoGAPS. As informed, the design discussions kicked off at a workshop in Copenhagen on 23 May with new partners entering the project. The project consortium consists of major industry actors: Global Maritime Forum, Mærsk Mc-Kinney Møller Center for Zero Carbon Shipping, Yara, BW Epic Kosan, MAN Energy Solutions, Wärtsilä and DNV.
 DSME installs the world's 1st high-manganese steel LNG fuel tanks on VLCC:
DSME installs the world's 1st high-manganese steel LNG fuel tanks on VLCC: South Korean shipbuilder Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME) and compatriot steel-making company POSCO have hit a new milestone in their technological collaboration to build eco-friendly dual-fuel propulsion vessels. After more than 10 years of joint research with POSCO, DSME applied high-manganese steel to LNG fuel tanks for the first time in the global shipbuilding industry. LNG fuel tanks are the core equipment for eco-friendly dual-fuel ships. On 16 June, DSME held a ceremony to install IMO Type-C LNG fuel tanks using high-manganese steel on a very large crude oil carrier (VLCC).

Tata Steel, Van Dam Shipping join forces to develop a hydrogen-fueled vessel: Indian steel-making company Tata Steel has entered into an agreement with Dutch firm Van Dam Shipping to develop a hydrogen-powered vessel. As informed, the vessel concept to be developed will have a loading capacity of approximately 5,000 tons and will be the first vessel of this type. According to Tata Steel, currently, the hydrogen-powered shipping sector includes inland waterway vessels and small ferries. Some of them are hybrids, while the others are partially hydrogen-powered or fully hydrogen-powered. With the new ship concept, the partners aim to reduce carbon emissions caused by the sea transport of steel.
Acta Marine orders methanol-powered CSOVs: The Netherlands-based maritime support provider Acta Marine has signed a contract for the construction of two next-generation, Methanol MDO/HVO-powered DP2 Construction Service Operating Vessels (CSOVs) at the Tersan Shipyard in Turkey. Acta Marine has also reserved options for two additional CSOVs for delivery at a later stage.

Howden's H2 compressors for the world's 1st carbon-neutral containership: Provider of air and gas handling products, technologies, and services Howden has been contracted by European Energy to supply a hydrogen compression solution that will deliver pure (green) hydrogen as feedstock to e-methanol production, fuelling world's first carbon-neutral boxship. Under the contract, the company will provide five compressor packages, which will deliver the required hydrogen purity, pressure, and flow capacity levels on demand.
MOL Conducts Carbon-offset Voyage with car carrier- offsetting CO2 emissions from Ocean Transport of completed cars for Europe: Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. announced that one of the company's car carriers completed a carbon-offset voyage for the ocean transportation of completed cars from Japan to Europe by using voluntary carbon credits (Note 1). This initiative was conducted as a pilot case to study the specific use of carbon credits in ocean shipping to compensate carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, which are difficult to reduce using currently available technology.
Shipyards
Approval for Japanese LPG-powered VLGC convertible to ammonia: Japanese shipbuilder Mitsubishi Shipbuilding, a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) Group, has completed the conceptual design of a very large gas carrier (VLGC) initially powered by LPG but adaptable to future use of ammonia as the main fuel. The shipbuilder has also received approval in principle (AIP) from the classification society ClassNK for the design. The design is expected to allow relatively small-scale ship retrofitting when the use of ammonia fuel becomes a viable option.

Fuels
Preparing for future fuel mix, Titan LNG rebrands as Titan: Dutch independent fuel supplier to the marine industry, Titan LNG, has decided to rebrand as Titan. As explained, the new name better reflects Titan's commitment to delivering all the fuels that decarbonize shipping and industry in a substantial way, such as liquefied biomethane (LBM), and any hydrogen-derived green fuel in the future. Titan specializes in providing shipping and industrial customers with end-to-end clean fuel solutions. This includes project planning, physical supply, and delivery, as well as risk management and hedging services to mitigate price fluctuations.

Biofuels
MSC launches biofuel campaign: MSC is launching a campaign to reach net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050 “Journey to Net Zero” and has announced it has adopted sustainable biofuel as a transition fuel in its ocean operations. MSC said biofuel is the only low-carbon fuel currently available that does not require any adjustment of its vessels' engines.
Available at selected world ports, MSC Biofuel Solution offers customers the opportunity to join forces with MSC to decarbonize their supply chains and achieve their climate targets. Specifically, MSC procures and bunkers low-carbon certified sustainable biofuel, derived from sources such as used cooking oil. This responsibly-sourced, second-generation biofuel comes as a blend with conventional marine oil and its biocomponent can reduce CO2 emissions by 90%.

Ports
Ports of Montreal, Québec, and Trois-Rivières look to jointly strengthen the St. Lawrence corridor: The Port Authorities of Montreal, Québec, and Trois-Rivières announced the creation of a working group to identify and facilitate the implementation of joint initiatives. The signing of a collaboration agreement between these three ports on the St. Lawrence River is motivated by strategic, environmental, and economic factors. The working group will explore different avenues of collaboration that could improve the competitiveness of the St. Lawrence corridors, such as the connection between the ports and freight and train transport networks, the exchange of expertise, or the compatibility of technological systems.
 Port of Helsinki eyes carbon neutrality by 2030:
Port of Helsinki eyes carbon neutrality by 2030: The Port of Helsinki said it is committed to promoting climate-friendly foreign trade and sustainable travel. The port is constantly making its operations more eco-efficient and strongly influencing the control of environmental impacts in its operating environment. The targets for the port's own emissions and emissions from ships were brought forward to 2030.
 Port of Long Beach joins the world's 1st transpacific green shipping corridor:
Port of Long Beach joins the world's 1st transpacific green shipping corridor: The US Port of Long Beach (POLB) has signed on to the Shanghai-Los Angeles green shipping corridor, a partnership of C40 Cities, ports, shipping companies, and cargo owners convened to create a zero-emissions transpacific trade route. First announced in January by C40 Cities, the ports of Shanghai and Los Angeles, and key maritime stakeholders, this green shipping corridor will be a big step toward decarbonizing shipping between the busiest ports in China and the United States. Moreover, it is one of the first green maritime routes announced following the signature of the Clydebank Declaration at COP26.

Regulations
IMO body grants green light to the proposal on curbing emissions from ships in the Mediterranean: The 78th session of the Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC 78) of the International Maritime Organization (IMO), which convened on 6-10 June 2022, approved the designation of the Mediterranean Sea Emission Control Area for Sulphur Oxides and Particulate Matter (Med SOx ECA) under regulation 14 of Annex VI to the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL). The formal designation of the Med SOx ECA will be put forward for adoption at the 79th session of MEPC due to take place on 12-16 December 2022.
Governments
New maritime innovation center to be established in the UK to support net-zero ambitions: Torridge District Council in the UK has voted to support a funding bid, seeking approximately £15 million ($18 million) to create the Appledore Clean Maritime Innovation Centre in northern Devon, with the aim of bolstering net-zero maritime ambitions in the region. The center, at Middle Dock, a site that neighbors the Harland & Wolff shipyard, is to establish northern Devon as a research and development space for collaborative next-generation maritime initiatives. It will include research and industry partnerships from the University of Plymouth and the Center for Future Clean Mobility (University of Exeter), as well as a range of offices, workshops, wet labs, and aquaculture tanks. The new facility will benefit from the University of Plymouth's knowledge and innovation in environmental intelligence, offshore renewable energy, clean maritime, and aquaculture.

Source: Maria Bertzeletou, Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com



















 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 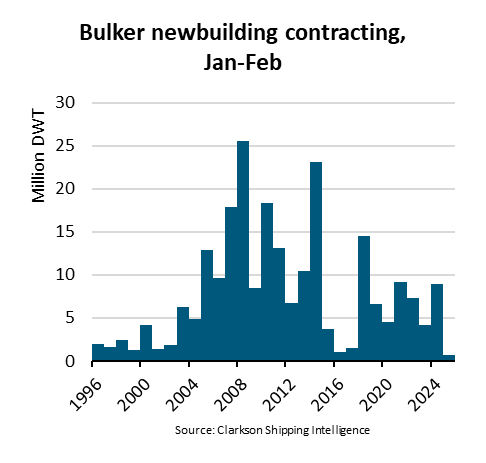 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar