Latest Trends on fuel transition, shipyard actions, government, ports, financing and industry players
Carbon capture is said to be the key to shipping's green transition. In a keynote address at the Posidonia conference, ABS chief Christopher J. Wiernicki announced that the class society believes that net-zero cannot realistically be delivered without efficient carbon capture and storage technology for ships. Onboard carbon capture and storage (OCCS) is a technology in the early stages of commercial development.
OCCS is already deployed in limited commercial operation by container feeder line JR Shipping, in combination with technology provider Value Maritime. Scorpio Tankers is working on a similar solution with American startup Carbon Ridge, with plans to install a small-scale test unit on one of Scorpio's vessels.
ABS said that it is developing comparable technology for an LNG carrier with DSME and GasLog. The three companies will develop an onboard CO2 capture and storage system (OCCS) to return CO2 from the exhaust gas back to the ship for storage. The stored CO2 can then be offloaded to shoreside facilities after entering the port. The three companies will design an OCCS for an LNG carrier, which will be built by DSME. Development work is expected to be completed by the first quarter of 2023. ABS will set up rules and regulations for OCCS development, provide technical advice, conduct risk assessments, and supervise testing leading up to approval in principle (AIP).
New Alliances for Decarbonization
BHP and NYK strengthen strategic partnership to progress shipping decarbonization: BHP and NYK have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to expand and deepen their existing business relationship and to support the decarbonization of ocean transportation across their shared supply chain. BHP and NYK will jointly study the next generation of zero-GHG emission ships fuelled by green or blue ammonia. If feasible, this could potentially support both organizations in their ongoing efforts to achieve their respective long-term GHG emission reduction targets for shipping and present a further decarbonization option for the shipping industry. BHP and NYK also aim to promote the use of GHG emission reduction measures such as energy-saving innovations and technologies, and alternative lower- and zero-GHG emission marine fuels.
 Berge Bulk and Kongsberg Maritime aim to advance decarbonization in shipping:
Berge Bulk and Kongsberg Maritime aim to advance decarbonization in shipping: Norwegian maritime technology group Kongsberg Maritime (KM) and Singapore-based dry bulk owner Berge Bulk have signed a memorandum of understanding to jointly develop and advance the deployment of decarbonization technologies onboard dry bulk cargo vessels. Berge Bulk has embarked on an ambitious environmental program that has produced ships like Berge Logan, described as “the most energy-efficient bulk carrier in the world”.
 KR, DSME join forces on digitalization, smart ship tech:
KR, DSME join forces on digitalization, smart ship tech: Classification society Korean Register (KR) has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with compatriot shipbuilder Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME), agreeing to work together on increased digitalization and the development of smart and autonomous ship technology. Under the MOU which was signed on 18 May, KR and DSME will form a joint council and cooperate on smart and autonomous ship technologies and digitalization research. With ‘digital and eco-friendly’ as a future keyword, KR launched its big data-based Integrated Survey Center (KR-ISC) last month. The development of, necessity, and demand for smart technology is a crucial global issue regardless of industry boundaries, the classification society believes.
 Port of Québec celebrates new partnership as RightShip supports EcoCargo emissions reduction initiative:
Port of Québec celebrates new partnership as RightShip supports EcoCargo emissions reduction initiative: RightShip, the world's leading maritime due diligence organization, is pleased to announce that the oldest port in Canada – the Port of Québec – joins a growing list of organizations using its proprietary greenhouse gas (GHG) rating tool, to assess the emissions of ships entering its waters. The Port now offers discounts on port fees to vessels, dependent on their GHG Rating and emission efficiency. RightShip's GHG Rating provides a transparent method to assess the relative efficiency of vessels and compare a ship's CO2 emissions relative to peer vessels of a similar size and type, using an easy-to-interpret A to G scale.

DNV, Saronic Ferries team up to develop electric ferry concept in Greece: Classification society DNV has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Greek ferry company Saronic Ferries to enable the development of an electric ferry for local deployment in Greece. The MOU was signed during the Posidonia 2022 trade fair being held in Athens from 6 to 10 June.
As explained, the collaboration is targeted towards a fully electric concept for deployment on shortsea passenger routes in the Argosaronikos area. The use of all-electric or hybrid vessels in the short sea ferry segment has surged in recent years as the benefits of the technology have been demonstrated in pilots and full-scale deployments.

MAN and Anglo-Eastern commit to Overridable Power Limitations for EEXI: MAN said its deal covers service installation of retrofit solutions developed for vessels in need of modification in order to meet upcoming IMO energy efficiency existing ship index (EEXI) regulations, including MC- and ME- engines. Anglo-Eastern has around 300 vessels in need of OPL solutions for mechanically- and electronically-controlled engines.
Industry Actions
Kongsberg Digital to digitalize nearly 500 MSC vessels: Norwegian digital solutions provider Kongsberg Digital and Swiss MSC, the world's largest container shipping company, have signed a contract for digitalizing MSC's entire fleet consisting of approximately 500 vessels with Vessel Insight. Being a founding member of the Digital Container Shipping Association (DCSA), MSC is already a digitally mature shipping company with many applications and systems in place. By using Kongsberg Digital's vessel-to-cloud data infrastructure Vessel Insight, MSC will be able to achieve more transparency and improved utilization of data.
 MSC Cruises targets zero-impact ops through six focus areas:
MSC Cruises targets zero-impact ops through six focus areas: MSC Cruises, a part of the Swiss-based shipping and logistics conglomerate MSC Group, has published its 2021 Sustainability Report highlighting the progress and laying the foundations for achieving zero-impact operations. The company chose 8 June, World Oceans Day, to publish the report claiming it has made significant progress in its sustainability practices despite the challenges brought by the pandemic in the past year. MSC Cruises developed the Sustainability Action Plan establishing six key work streams across the business. These include transitioning to net-zero emissions, scrutinising resource use and waste, supporting people, investing in sustainable tourism, building greener terminals, and procuring sustainability.

Capital Ship Management to drive fleet decarbonization with ABS My Digital Fleet: The agreement is the latest investment by Capital towards decarbonizing its operations, following the recent announcement securing ABS notations and recognizing investment in decarbonization technologies for its newbuild orders for medium-range tankers.
EMINOX releases the latest white paper on emissions regulations in the global shipping industry: A leading designer and manufacturer of emissions technologies and solutions have released its latest white paper which tackles the challenges of compliance and emissions regulations in the global shipping industry. Exploring the latest regulations and legislation and the myriad implications for the global shipping industry, the paper supports all sectors to understand what is required and how compliance can be achieved.
Technology
WinGD launches a software-based solution for EEXI compliance: Swiss marine power company WinGD has launched a software-based Engine Power Limitation (EPL) system to enable rapid and cost-effective compliance with the IMO's EEXI regulations, which enter into force next year. The solution uses the engine control system to limit engine power to meet EEXI design efficiency baselines and includes a required emergency override capability. It is applicable to all WinGD, Wärtsilä and Sulzer X, X-DF, and RT-flex two-stroke engines operating with UNIC or WECS-9520 engine control systems.
 Høglund systems help power the world's largest ethane carrier:
Høglund systems help power the world's largest ethane carrier: The Norwegian integrated automation and energy specialist Høglund Marine Solutions has delivered an automation and control system for the Pacific Ineos Belstaff, the world's largest ethane carrier. During the project, Høglund designed an integrated automation system with a ship performance monitor and a customized control system. According to the company, the technology was created to support Babcock LGE's cargo handling system (CHS) and fuel gas supply system (FGSS) for the vessel, and it was completed in 18 months.
 JR Shipping:
JR Shipping: Six more ships to use Value Maritime's filter and carbon capture system: Dutch shipping company JR Shipping has contracted compatriot technology firm Value Maritime to retrofit another six vessels with the latter's exhaust cleaning Filtree and carbon capture system, making almost the entire fleet sustainable for the future. Over the past three years, JR Shipping and Value Maritime have been consistently working on reducing carbon emissions, lowering the fleet's environmental footprint, and staying ahead of IMO targets. Both companies are building momentum and combining their knowledge and resources to take significant steps in the emission reduction and decarbonization of short sea shipping.

Next Generation of Vessels
MOL names third Eenex next-gen coal carrier: The Japanese shipping company has held a naming ceremony for the third vessel in the EeneX series of next-generation coal carriers. During the ceremony, which took place on 9 June at Namura Shipbuilding, the vessel was named Energia Azalea. The carrier was built to serve Japanese energy company Chugoku Electric Power by transporting coal from overseas to its power stations and contributing to a sustainable and stable supply of electricity. The 99,965 dwt carrier is the third in the EeneX series of next-generation coal carriers based on the Japanese shipbuilding industry's accumulated know-how and technology in developing and constructing coal carriers, along with MOL's expertise in operating these vessels.
 ABS approves SHI's ammonia-fueled Neo-Panamax containership design:
ABS approves SHI's ammonia-fueled Neo-Panamax containership design: South Korean shipbuilder Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) has received approval in principle (AIP) from the classification society American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) for its design of an ammonia-fueled Neo-Panamax container vessel. The approval was presented at the Posidonia International Shipping Exhibition. It confirms the design has been reviewed by ABS against the requirements outlined in the ABS Guide for Ammonia Fueled Vessels.

Eastern Pacific Shipping to order ammonia carrier from Hyundai Heavy: Singapore-based shipping company Eastern Pacific Shipping (EPS) intends to order an ammonia dual-fuel gas carrier which will be built at the Korean shipyard Hyundai Heavy Industries. Eastern Pacific Shipping, the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA), Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI), and the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) signed a memorandum of understanding for this ocean-going ammonia dual-fuel gas tanker. The vessel will be registered under the Singapore flag. ABS will class it, and it will be the first vessel with MAN Energy Solutions G60 two-stroke dual-fuel ammonia engine.
LR and Samsung Heavy Industries pen MOU for Samsung autonomous ship: LR and Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to develop an autonomous ready ship design to support maritime digitalization and the growing demand for operational benefits of increased autonomy.
SAS (Samsung Autonomous Ship) is an autonomous navigation system that integrates current navigation equipment, such as ECDIS with TCS (Track Control System), RADAR, CONNING, and remote-controlled BMS, with SHI's new SVISION® system, using technology to eliminate human error which accounts for most maritime accidents.
Hyundai Glovis to develop the world's largest CO2 carrier: Shipyard Hyundai Heavy Industries is working with compatriot owner Hyundai Glovis to develop the world's largest carbon dioxide carrier. Class society ABS is on board the project to create a 74,000 cu m CO2 carrier, far larger than anything thus far announced in the nascent CO2 trades.
 CMA CGM orders its first methanol-powered containerships:
CMA CGM orders its first methanol-powered containerships: French shipping and logistics major CMA CGM has placed its first order for methanol-powered vessels to expand its energy mix and become carbon neutral by 2050. The company revealed it decided to order a total of six 15,000 TEU dual-fuel methanol-powered containerships from an unnamed shipbuilder. The newbuilds are planned to join the CMA CGM fleet by the end of 2025. The French company has been so far primarily focused on ordering LNG fuelled vessels to reduce atmospheric pollutant emissions. However, it is now diversifying its energy sources by joining its counterpart Maersk in ordering a methanol-powered fleet.

Shipyards
Shipbuilders proceed with designs for ammonia-fueled ships: The shipbuilding sector continues to report strong progress in developing future designs to use ammonia as the primary fuel. Designers are working to develop ships in each of the primary categories that in the future will be able to use the new fuels and provide shipowners a viable migration path to future-proof current investments in ships. Japan's Mitsubishi Shipbuilding and South Korea's Samsung Heavy Industries each reported design approval for additional ships designed to employ ammonia as their primary fuel.
Mitsubishi Shipbuilding designs LPG-powered VLGC convertible to ammonia fuel: Japanese shipbuilder Mitsubishi Shipbuilding, a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) Group, has completed the conceptual design of a very large gas carrier (VLGC) initially powered by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) but adaptable to future use of ammonia as the main fuel. The shipbuilder has also received approval in principle (AIP) from compatriot classification society ClassNK for the design. According to Mitsubishi Shipbuilding, the creation of a design enabling conversion to ammonia fuel in line with future needs is expected to permit relatively small-scale ship retrofitting when the use of ammonia fuel becomes a viable option.
Mitsubishi Shipbuilding gets BV AiP for LCO2 spherical cargo tank system: Classification society Bureau Veritas (BV) has delivered approval in principle (AiP) to Japanese shipbuilder Mitsubishi Shipbuilding – part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) Group – for a spherical cargo tank system for liquefied CO2 (LCO2) carriers. Mitsubishi Shipbuilding has developed a new spherical cargo tank system for LCO2 carriers, applying its technologies in structural analysis and material evaluation cultivated through the design and construction of liquefied natural gas (LNG) carriers equipped with spherical tanks.

Fuels
DNV and LR approve methane abatement technology design to reduce slip: One of the challenges to the future of liquified natural gas as a maritime fuel and a major point of contention from the environmental community is methane slip where unburnt LNG is released into the environment. A Swiss-based climate tech company, Daphne Technologies, reports that it has received design approvals from both DNV and Lloyd's Register for a methane abatement technology that addresses the issue. Using a plug-and-play approach, Daphne Technologies reports its solution reduces over 90 percent of methane slip from LNG-powered engines, providing a life extension to LNG as a marine fuel, and a clear pathway to carbon neutral shipping industry.
Biofuels
Capital, LR to advance marine biofuels research in a new pilot project: Greek ship management company Capital Ship Management (Capital) and classification society Lloyd's Register (LR) has agreed to trial the use of biofuels in a new pilot project to support the maritime industry's research for low to zero-carbon fuels. The trial is said to be in line with the International Maritime Organisation's (IMO) greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction targets. Under the project, biofuel-blended marine fuel will be tested on Capital managed 300,000 dwt crude tanker, Appollonas.

Ports
American hydrogen company Plug Power to build a large-scale green hydrogen plant at Port of Antwerp-Bruges: Plug signed a 30-year concession agreement to build the plant at the Belgian port, the second largest in Europe. The company plans to build a 100-megawatt green hydrogen plant, using its own electrolyzer and liquefaction technology. It leased 28 acres of land under the agreement. Therefore, Plug will produce up to 12,500 tons per year of liquid and gaseous green hydrogen for the European market. Construction of the plant will begin upon completion of the permitting process in late 2023. Initial production of green hydrogen is to start in late 2024, and plant commissioning will take place in 2025.
 Barcelona plans the first "emissions tax" on Cruise Ships in 2023:
Barcelona plans the first "emissions tax" on Cruise Ships in 2023: Barcelona has become the first to propose an "emissions tax," specifically for cruise ships visiting its port. A popular cruise destination and one of Europe's busiest ports, environmental activists have previously criticized Barcelona for having high levels of carbon emissions and air pollution. Specifics of the planned tax have not been announced, but it will be in addition to other taxes placed on tourists visiting the popular destination. The tax will be introduced in 2023.
 Port of Gothenburg first to provide shore power for tankers:
Port of Gothenburg first to provide shore power for tankers: As part of a plan to provide shoreside power for tankers berthed at the Energy Terminal, the Gothenburg Port Authority has created a new concept that makes the system safe, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective. As informed, the port has teamed up with shipping companies on the island of Donsö, national and European ports, classification societies, local oil companies, and the Swedish Transport Agency. The aim is to set a new global standard for shoreside power for tankers berthed in a hazardous environment.

Regulations
EU delays ETS plans for shipping: The European Parliament unexpectedly rejected a proposal to upgrade the European Union's Emissions Trading System (ETS) last Wednesday. The unexpected rejection seems to be caused by disagreements over climate ambitions. The main disagreement concerned the share of quotas and the emissions reduction targets in the system. According to current reports, the inclusion of shipping into the ETS does not seem to have raised major debates, despite the that the European Parliament's environmental committee (ENVI) some weeks ago voted to speed up the inclusion. According to Reuters negotiators will attempt to reach a new deal by June 2023. EU is racing to finish the law this year so that it can apply in 2023.
IMO's international carbon intensity measurement rules need a rethink: Shipping needs to smarten up its emissions rules if it is to decarbonize effectively, with the International Maritime Organization's new carbon metrics a prime candidate for review given the potential for unintended consequences, Eman Abdalla, global operations and supply chain director at Cargill Ocean Transportation, told S&P Global Commodity Insights on the sidelines of the Posidonia shipping industry event in Athens June 9.
Five more countries back the 2050 zero shipping emissions target at the UN: At least five more countries now support aligning the IMO's climate goals with the Paris Agreement. The Cook Islands, Mexico, Myanmar, Colombia, and Malaysia publicly endorsed the 2050 zero shipping emission target for the first time at MEPC 78. Delegates debated revising the IMO's current climate strategy and will continue the negotiations at MEPC 79 in December while gathering for additional working group talks (ISWG-GHG) beforehand.

Governments
U.S. government to fund $8 billion program to develop clean hydrogen hubs: The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will fund the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law's $8 billion program to develop regional clean hydrogen hubs (H2Hubs) across America. On 6 June 2022, DOE released a notice of intent (NOI) to fund the H2Hubs program. H2Hubs will create networks of hydrogen producers, consumers, and infrastructure to accelerate the use of hydrogen as a clean energy carrier.
DOE says the production, processing, delivery, storage, and end-use of clean hydrogen is crucial to its strategy for achieving President Biden's goal of a 100 percent clean electrical grid by 2035 and net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
Source: Maria Bertzeletou,Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com





















 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 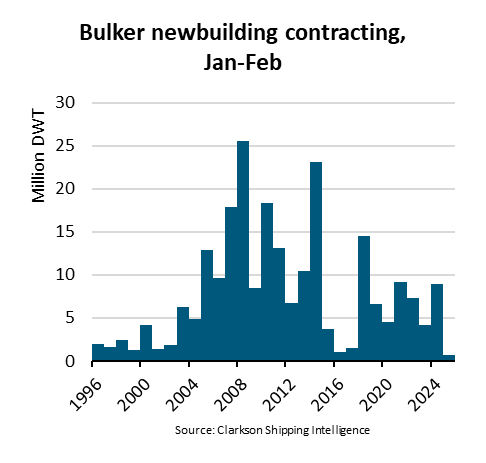 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar