
Trucks arrive to pick up containers at the Port of Los Angeles in Los Angeles, California, November 22, 2021. [Photo/Agencies]
Los Angeles and Shanghai, home to the largest ports in the United States and China, are working together to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from cargo traffic between them.
The initiative, which will create a "green shipping corridor" billed as the first of its kind, is at the heart of a recently announced partnership between the ports of the two cities and other stakeholders in the industry that aims to shift to zero carbon-fueled ships by 2030 and reduce emissions from port operations.
"We are just getting started on this important work, but by convening international coalitions of key goods-movement stakeholders such as cities, ports, shipping lines and cargo owners, we hope this groundbreaking green shipping corridor initiative will catalyze action on a global scale," Alisa Kreynes, green ports program manager at C40 Cities, a climate group, told China Daily.
The initiative was made possible by Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti, who launched the C40 Green Ports Forum while serving as the chair of C40, a network of mayors from leading cities around the world, she said.
The global shipping industry depends heavily on oil and is responsible for 3 percent of global emissions annually. It has come under increasing pressure to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions.
To keep global warming below 1.5 C, an ambitious target set by the Paris Agreement, Kreynes said it is important to decarbonize the shipping sector, especially along major routes such as the Trans-Pacific corridor, where ships moved 21 percent of the world's container volume in 2020.
"For the past 20 years, the Port of Los Angeles has been the busiest container port in the Western Hemisphere; its top trading partner is China in terms of cargo volume," Kreynes said. "In terms of container throughput, the Port of Shanghai is the world's largest port."
Ken Alex, director of Project Climate at UC Berkeley's Center for Law, Energy & the Environment, said it is encouraging to see two of the world's largest ports work collaboratively to accelerate the transition to zero emission fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. "It is of particular note that Shanghai and Los Angeles will develop best management practices which can be used by other large ports around the world," he told China Daily.
According to Alex, shipping emissions from ports account for an estimated 18 million metric tons of carbon dioxide annually and are on a trajectory to increase fourfold by 2050. That makes a concerted effort to reduce those emissions by two major ports a positive development, he said.
"US-China climate change collaboration can be significantly enhanced through subnational cooperation, such as state-province agreements and pilots, city-to-city exchange and port-to-port partnerships, such as the LA-Shanghai Trans-Pacific Green Shipping Corridor. These efforts benefit all," Alex said.
Ingrid Irigoyen, director of the Aspen Institute's Shipping Decarbonization Initiative, a participating partner in the plan, told China Daily that the hope is for this collaboration to bring together the private and public sectors to create "enabling conditions" for emissions reduction and new technologies that "offer a pathway to commercially viable zero-emission shipping".
"We also look forward to this partnership inspiring confidence among policymakers around the world to provide strong support for the transition to zero-emission fuels and technologies," Irigoyen added.
Phillip Sanfield, a spokesperson for the Port of Los Angeles, said it has enjoyed a "long-standing relationship" with the Port of Shanghai.
"It's important for these two ports to send a signal to the rest of the world that reducing gas emissions in the maritime industry is critically important," he told China Daily.
Noting that the two ports and C40 Cities will work out details for the plan over this year, Sanfield said more information about it will be shared in the coming months.
"The Port of Los Angeles and our counterparts in Shanghai have worked together on other environmental initiatives over the years. Sharing best practices and offering assistance is something we value very much," he said.
A "green shipping corridor implementation plan" for the initiative is expected to be developed by the end of 2022, according to partnership officials. Some key goals of the partnership include the phasing in of low, ultralow and zero-carbon fueled ships through the 2020s, the development of practices to reduce emissions for ships using the corridor, a reduction in supply chain emissions and an improvement in air quality in the ports and adjacent communities.
Source: Chinadaily
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com


 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 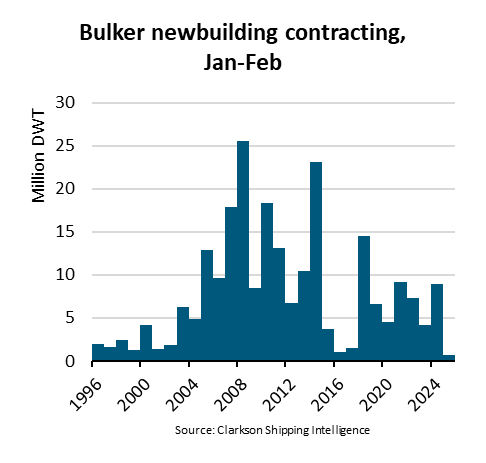 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar